SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is about implementing various techniques to improve your website’s visibility in search engines (Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo and so on). Since people spend increasing amounts of time online, SEO is a must-have if you want to reach your target audience.
Did you know that:
- Over 90% of all online activities start with a search engine. (Webfx)
- The top position on Google receives ten times more traffic compared to position 10 (the bottom placement on the first page). (OnTheMap)
- 53.3% of all traffic to websites comes via organic (unpaid) search results. (Brightedge)
SEO helps you tailor your content, optimizes your website in order to ensure that visitors and Google appreciate your work. This leads to increased visibility, brand awareness and ultimately, more customers.
Table of Contents
About the guide
The internet is flooded with information and competitors, and it’s a real challenge to stand out from the crowd. This guide will give you the tools you need to achieve the coveted top spot on Google. We will explore what SEO is, why it is important and what you can do to get more traffic from Google. The guide is divided into three main areas:
- Technical SEO – How search engines find and index the content on your site. Technical SEO also includes elements such as loading times and adapting the website to different device types (desktop, mobile and tablet).
- Content – How to create content rewarded by both users and search engines.
- Off Page SEO – How to boost your website’s credibility through references. More than anything, getting links (backlinks) from other websites are key in this endeavor.
We will cover these three areas in depth, as well as how to set up a successful SEO strategy.
Tip: Watch our webinar on SEO Basics, if you didn’t do it already:
What is a search engine?
A search engine is a digital tool used to search for information. When people think of search engines, Google and its competitors (Yahoo, Bing, DuckDuckGO, and others) tend to be the first to come to mind. These are called universal search engines, since you can use them to basically search for anything.
Source: Google’s search engine
Besides universal search engines, there are more specialized services, which basically function as search engines or even have integrated search engines in their service.
- Library search services – To find publications and books.
- E-commerce platforms, such as Amazon, often have their own search engines to find products or shops.
- Streaming services like Spotify, Youtube, Netflix, and others have search engines – often to find specific titles or genres.
Source: Amazon’s search engine
The focus of this guide is universal search engines and Google in particular.
The purpose of a search engine
The amount of information available on the internet is growing by the day. All of this data needs to be sorted and presented in a comprehensible way in order to make it make it manageable for people to navigate. This is where search engines come into the picture.
The purpose of a search engine is to help users easily find information they are looking for. Since it’s common that there are many pages on the same topic, it is important for search engines to prioritize:
- The most credible and relevant sources of information: Websites which are trusted in the field and whose content answers the questions best.
- User-friendly websites: Besides just answering questions, sites must also do so in an easily accessible and user-friendly way.
How do search engines make money?
The search engines operate financially through paid ads, which are relevant to the search inquiry of the user. This allows businesses to reach potential customers through both organic search results (the unpaid rankings) and ads.
Two ways of being visible
For businesses, search engines are a crucial platform to reach their target audience. When a potential customer searches for a product, service, or solution, it is important to be among the first results. Websites can appear in two ways in search engines:
- Organic search results: Appearing in search engines without paying for it. Through SEO, businesses can improve their visibility and rank higher in search results. Users consider organic search results more credible than ads.
- Paid advertising (PPC): Search engines also offer paid ad placements. These ads can be targeted based on a number of factors such as keywords, demographics, location, and user behavior. PPC gives businesses an opportunity to showcase their brand or offering to potential customers when they are actively searching for related products or services.
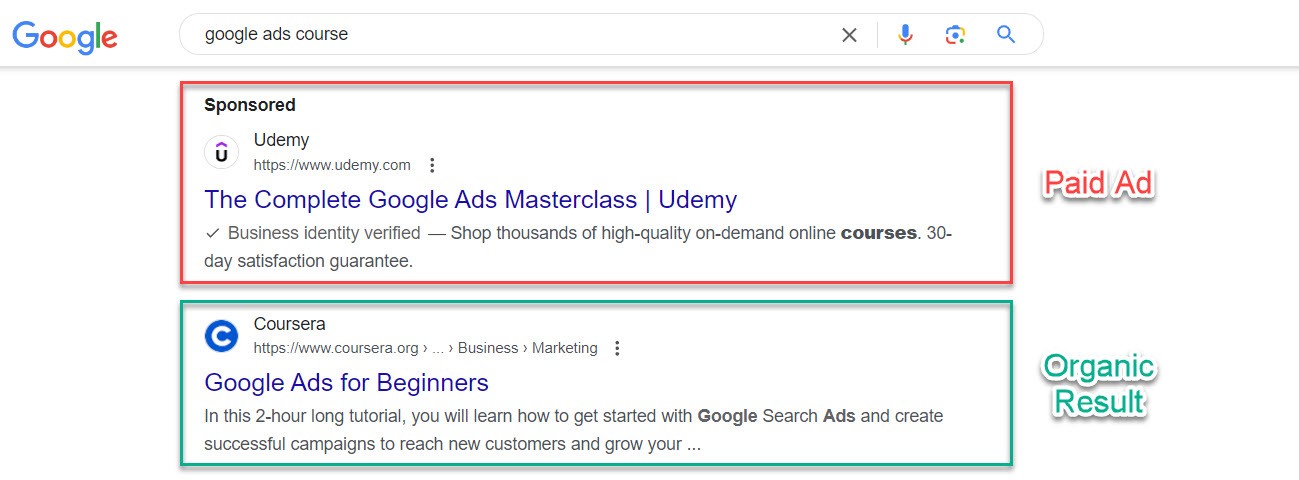
Later in this guide, we’ll look at organic and paid search results in depth and how they relate to each other.
The SEO industry
The increasing importance of online visibility has led to the emergence of an entire industry dedicated to understanding and optimizing for search engine algorithms. The industry is composed of a diverse range of services from specialized agencies and consultants to tools and platforms – all of them with the common aim of improving SEO. This emerging industry has created job opportunities, innovations, and has changed the way we think about digital marketing.
Understanding search engines
Whether you are a business owner, blogger, researcher, or artist, you want people to see and notice your work. Search engines are the primary source of web traffic. Without an understanding of how search engines work, you risk missing out on a large portion of your potential customers.
How does a search engine work?
Search engines apply sophisticated processes and algorithms to find and present content to users.
They start by sending web crawlers, or spiders, to systematically scan the internet for data. This data is then stored in a large database called an index.
The data in the index is then used to produce answers for users when they query the search engine.
In order to know which pages in their index is the right ones to display for a particular search inquiry, search engines use different algorithms.
The algorithms in a search engine
When users search for something, the search engine processes the query by comparing it with the contents of its index. It then applies a series of algorithms to determine the most relevant pages for the user’s search query.
Search engine algorithms are complex systems considering hundreds, if not thousands, of different factors to determine the relevance of pages. Some of the most important ones are:
- The presence of the keyword in the content
- The quality of the content
- Backlinks to the page – acting as votes of confidence
The underlying mechanisms and algorithms are constantly evolving to ensure quality and penalizing websites manipulating their way to better results. It’s important to stay up to date with the latest SEO trends and algorithm updates, in order to give your website the best conditions for success.
Google and other search engines are always cautious about sharing exact information on how the algorithms work. Accordingly, experimentation, testing, and anecdotal evidence is commonly applied when SEO experts try to understand the algorithms.
Major algorithm updates
Google, the world’s most popular search engine, has developed and implemented a number of major updates to its algorithm over the years to improve and fine-tune search results. Some of the most notable ones include:
PageRank: This is one of Google’s foundational algorithms. It assesses the quality and number of links to a page to estimate the importance and credibility of a page.
Panda: Launched in 2011, the Panda update penalizes sites with low-quality or ‘thin’ content, while rewarding sites with detailed and relevant content.
Penguin: This update was introduced in 2012 to identify and disadvantage websites using manipulative linking strategies to increase their ranking in search results.
Hummingbird: Launched in 2013, Hummingbird focuses on understanding search queries holistically instead of focusing on individual keywords. The update was launched with the aim of understanding the intent behind a search.
Mobilegeddon: Launched in 2015, this algorithm update prioritized mobile-friendly websites in search results and especially when searches were made from mobile devices.
Medic Update: Rolled out in August 2018 and mainly affected the healthcare sector. And particularly sites that did not follow Google’s EAT (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines.
BERT: Introduced in 2019, BERT focuses on understanding the context of words in search queries and offering more accurate results, especially for longer conversation-like searches.
Product Reviews Update: Launched in April 2021 with the intention of highlighting established expert opinions and reviews over pages merely collecting and summarizing ratings and reviews.
Page Experience Update: Rolled out between 2021 and 2022, this introduced Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor.
Helpful Content Update: The first Helpful Content (HC) update appeared in August 2022 and is about Google promoting helpful content, written by people, for people.
Google is constantly rolling out new and refined updates with the purpose of being the most relevant and credible search engine. Thus, as a digital marketer, it is crucial to stay up to date with ongoing updates.
Examples of search engines
The most popular search engine in the world at the time of writing is Google. It is known for its speed, accuracy and minimalistic interface. Here are some other major search engines:
Bing: Developed by Microsoft, Bing is an alternative to Google. It is the default choice on Windows devices.
Yahoo! Search: Although its popularity has waned over time, Yahoo! was once one of the biggest players.
Baidu: Baidu, the leading search engine in China, offers a range of services similar to Google but is tailored to the Chinese market.
DuckDuckGo: This search engine is known for its focus on user privacy and does not track user activity, providing a more private search experience.
Source: Yahoo’s search engine
How answers are presented in search engines
When you enter a search query into a search engine like Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo, the search engine analyzes billions of web pages in its index to find the most relevant results. These results are usually presented in a list form on a scrollable page. This is often referred to in technical terms as a Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Each item in the SERP is called a ‘search result’. A typical search result contains the name of the site, the title of the web page, a short description or extract of the content and the URL (web address).
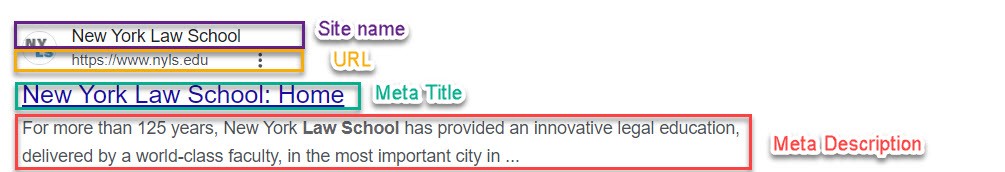
Different types of search results
In addition to organic search results, the SERP can include paid ads, local map listings, images, videos and other specialized results. Search results are generally designed to as relevant as possible to the query.
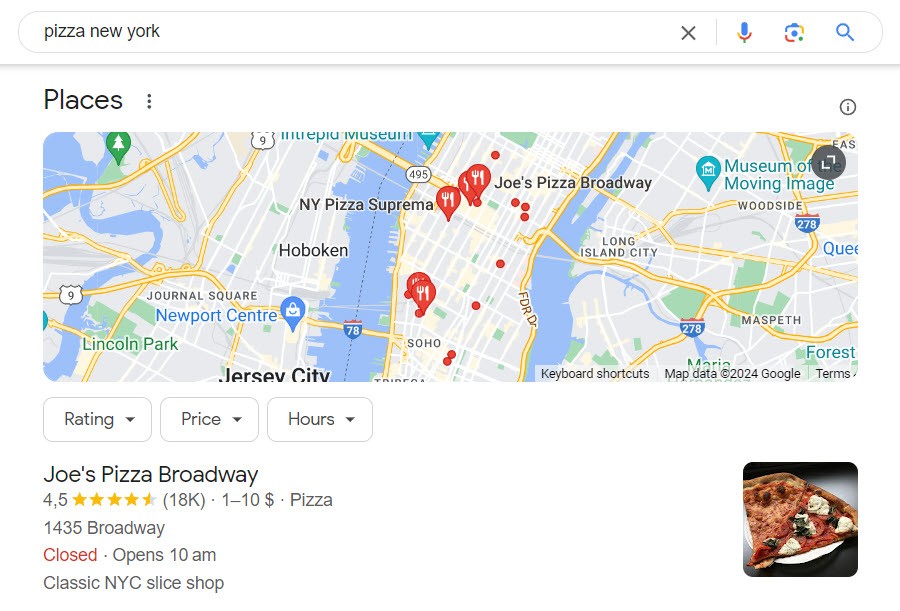
Example of search result showing a map pack
SEO: Basic insights
To summarize this section, SEO, or search engine optimization, is a set of techniques used to improve a website’s position in the SERP with the ultimate aim of attracting more organic traffic.
Search engines need to initially find your content and then algorithms will judge its relevance to decide where to rank the page. In this guide, we’ll go through the different elements of SEO that will help you optimize your website for the algorithms:
- Technical SEO
- Content
- Off Page (links)
But first, it’s important to understand why you should do SEO. This will help you prioritize the work ahead or to justify to colleagues and management why you need to work on it.
Why should you do SEO?
In this part of the guide, we will look at the potential impact of SEO. In the long term, it is a more sustainable strategy than paid advertising and a great way to increase brand awareness.
Why don’t companies do SEO?
Despite the benefits discussed in this guide, SEO is often an overlooked and under-invested activity for many businesses. This can be for reasons such as:
- Poor level of knowledge: They haven’t taken the time to learn about SEO and don’t understand its benefits. If you are one of those people, we hope this guide will clear up your questions.
- The results are not immediate: Unlike paid marketing, it often takes time before you get the traffic you’re seeking. We talk more about this below, under SEO vs PPC (paid advertising), and how you should plan your SEO efforts.
- It’s hard to keep up with new developments: Google continuously updates its algorithm, sometimes several times a day. Most of the time, it’s a matter of fine-tuning, but techniques which improved rankings 10 years ago may not work at all today. Worst case, they can lead to worse rankings. We will look at what’s happening today and what you can do to stay up to date.
- Other priorities: Working on SEO requires dedicating resources to it, and companies often choose to prioritize other initiatives. This is often linked to point 1, the lack of knowledge of decision makers.
Below we give you the tools to convince your company to put SEO on the agenda.
Why should you work on SEO?
The most important reason to invest in SEO is that it will bring more traffic to your website without you having to pay for it. If you do the work properly, it will also yield a number of other positive effects for you:
- Unpaid exposure for your brand, which is perceived as more credible from a customer’s perspective.
- Increased traffic on important keywords for your product/service.
- A more user-friendly site, which helps you increase conversions.
Google’s algorithm is designed to show the most relevant, organic answers at the top. That is, the pages that best answer the searchers question. By definition, SEO-friendly content is also user-friendly.
Why is a good position on Google important?
The higher a website ranks in Google’s results on a given search, the bigger is the chance that a user will click on it. This is known as the Click Through Rate (CTR).
A study from Backlinko shows that the top 3 organic results receive 54.4% of all traffic from Google. See the graph from the study below:
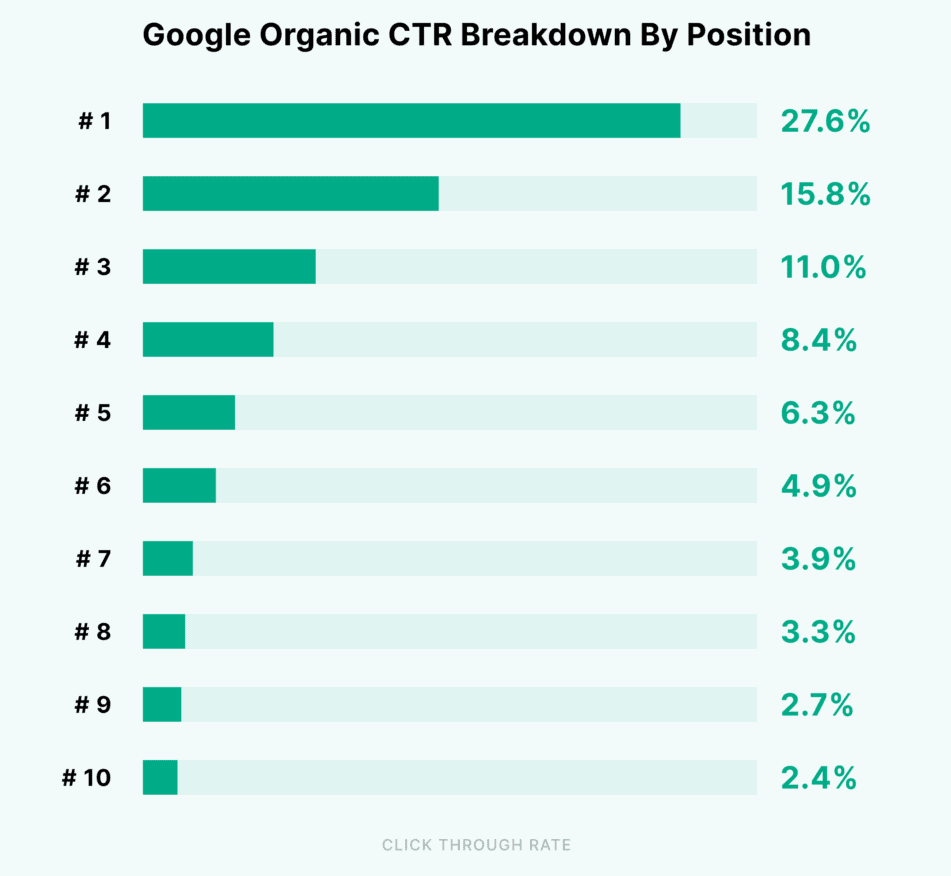
Source: Backlinko
As you can see, the amount of traffic drops drastically from the first position and below.
The recurring joke in the SEO industry is “The best place to hide a corpse is on page two of Google”.
But what about the adverts?
As you’ve probably noticed when googling, ads often appear before the organic results. Yet, people rarely click on them:
- Average CTR for organic position 1: 27.6% (data from backlinko)
- Average CTR for google advert on position 1: 2.2% (data from first page sage).
It can be insightful to consider your own experience. How do you act in relation to the search results? It’s probable that you, like most people, ignore the ads and click on the first organic result if it seems relevant.
We’ll come back to the comparison between organic and paid traffic later in the guide.
How many people use Google (and other search engines)?
The majority of the world’s population use search engines regularly. 82% of people between 18 and 64 years old to be exact. And the most popular search engine by far is Google, with a market share of almost 93%. The closest competitor, Bing, is not even close:
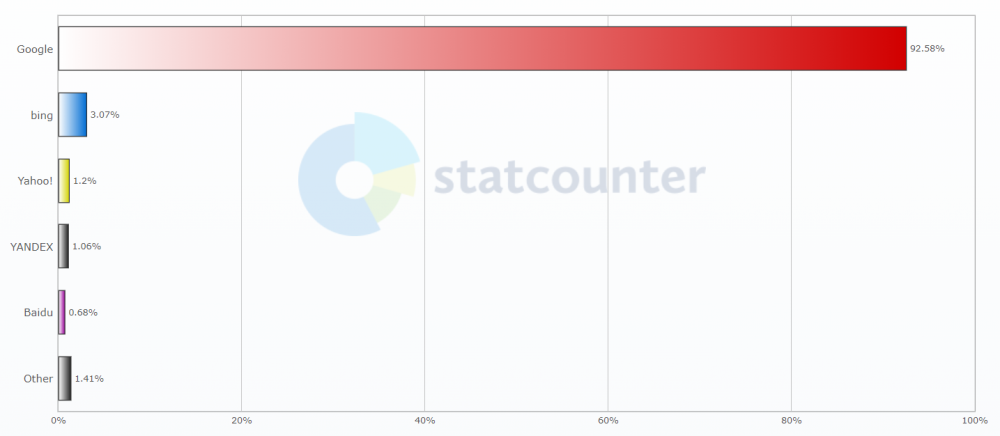
Source: Statistics from Statcounter
Because Google is so dominant, SEO work focuses almost exclusively on getting better rankings and more traffic from Google.
Most of the other search engines have similar algorithms governing rankings. If you get it right on Google, chances are you will drive traffic from Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, and others.
Do people trust Google?
We’ve found that people trust organic results the most, especially those that rank the highest. But what about trust in Google itself? A 2021 US study by SEOClarity found that Google was the tech giant most trusted by respondents.
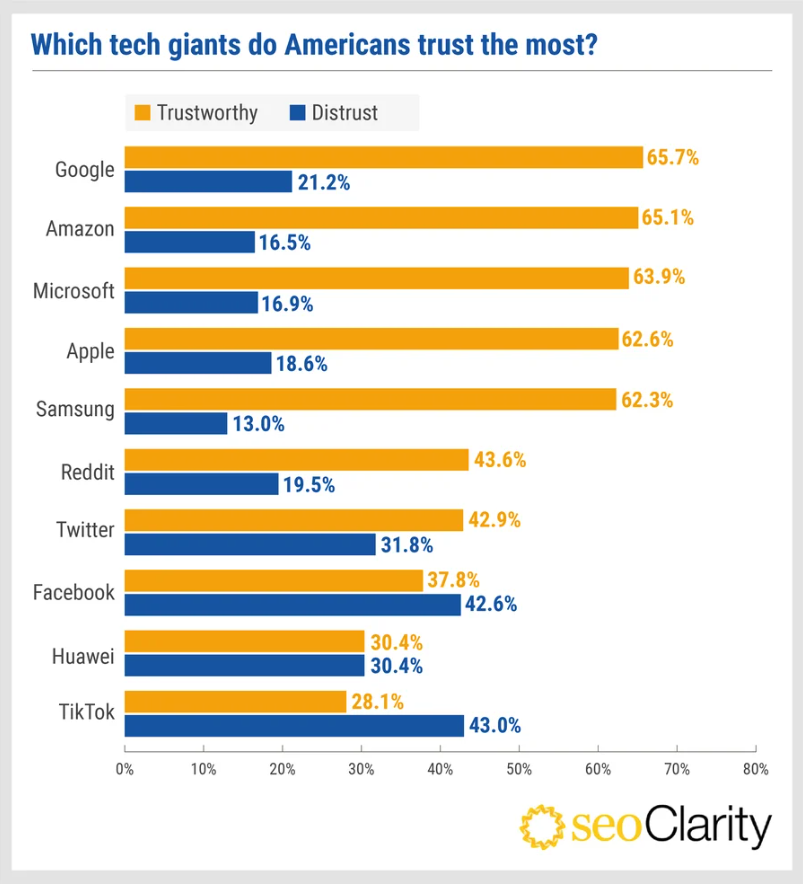
Source: Graph from SEOClarity
According to a study by Edelman, one of the world’s largest PR agencies, people trust search engines more than some news media.
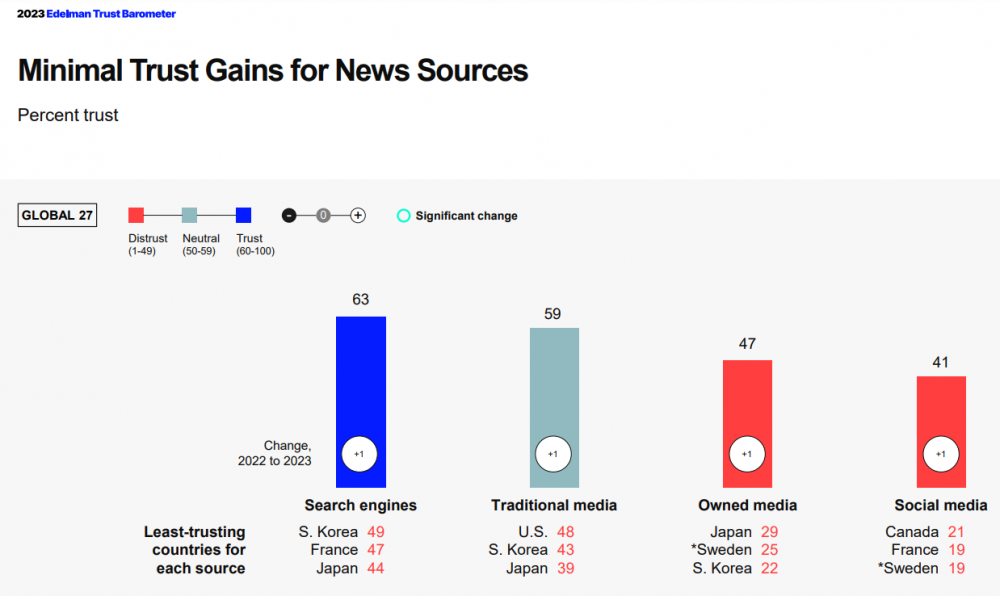
Source: Edelman Trust Barometer 2023
If your site appears at the top of Google, it’s not just a traffic driver. It’s also an indicator of quality and authority.
Google’s many faces
Google is constantly evolving to become a one-stop-shop for as many types of searches as possible. 2005 saw the launch of Google Maps, which has almost fully replaced address directories, since it provides directions so effectively. Google Flights and Google Hotels make it easier to search for and book hotels and flights, and Google Shopping helps you find what you are looking for in e-commerce.
Source: Google Flights
It is important to identify which of Google’s products are relevant to your business before optimizing for them. If you own a restaurant without having created a Google Business profile, you will never get any visitors through users searching on Google Maps. We take a closer look at Google Business and the map searches below.
Google Maps SEO
Google Maps is a must for all businesses and organisations with any kind of local presence and an emphasis of location-based customers. People use the map just like a regular search. They search for “Restaurant Copenhagen”, “hairdresser near me”, “car mechanic” and so on. If you do not appear on the map with your service, you do not exist.
Source: Google Maps
According to a survey by Zipdo, Google Maps is the world leader in map search with a market share of 70 %. The same survey also showed that 83% of users considered Google Maps to be essential to their decision-making process.
Google Business Profile
To be visible on the map search, you need to create a Google Business Profile. This is a kind of digital console where you fill in all the essential information about your company’s physical locations. Google then uses this information to display the locations in the map search.
Just like in Google’s regular search, the highest organic results below the “Sponsored Link” receive the most visits. Therefore, it is important you make sure to optimize your locations as much as possible.
To assess the relevance of businesses to the map search, Google looks at, among other things:
- Whether the company has entered the correct sector and business areas in the console.
- Customer ratings and reviews.
- Whether companies respond and interact with their reviewers.
- Whether contact and address details on Google match those on the company’s website, Facebook, and other credible digital records.
Keep up with the changes
Google is the most widely used and trusted source of information in an increasing number of areas, and the organic results are by far the most visited. So it’s important to keep up with the evolution of Google’s products and what it takes to get noticed. If you don’t do it, your competitors will do it, and you will definitely fall behind.
Google themselves are very good at communicating their products, updates, and their implications. You can find information here:
https://developers.google.com/search/blog
Other good external sources for staying updated are:
If you don’t have time
Businesses often find that the hardest part of SEO is keeping up with new developments. If you don’t feel like you can do it, or don’t have the time, getting help from an SEO agency or consultant can be a good option.
SEO vs PPC (Google Ads)
Previously in this guide, we briefly visited the difference in click-through rate (CTR) for organic positions and paid ads. Looking at numbers, it seems obvious that you should focus on SEO:
- Average CTR for organic position 1: 27.6% (data from backlinko)
- Average CTR for google advert on position 1: 2.2% (data from first page sage).
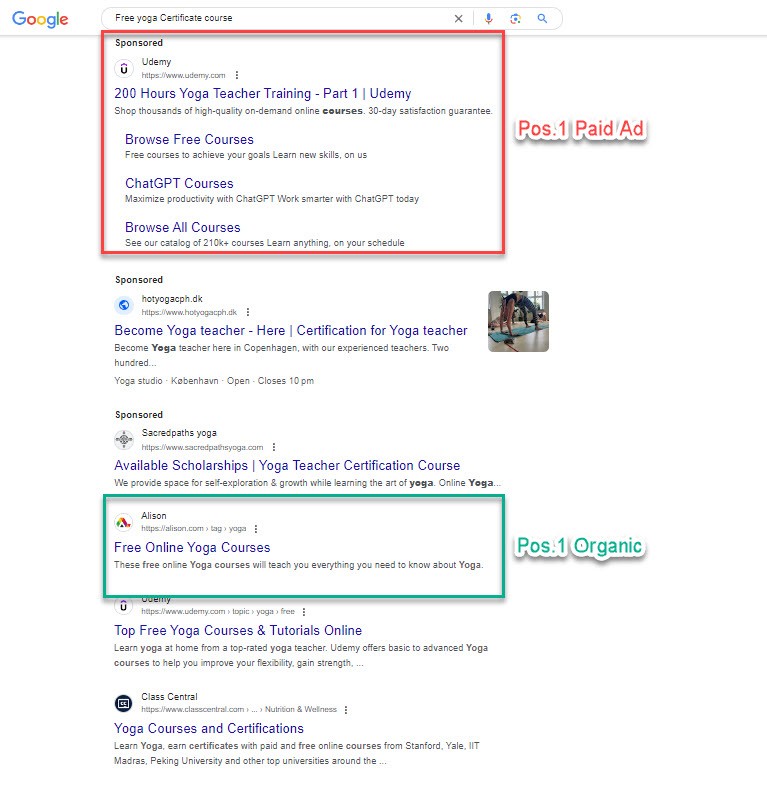
The reality is, as is usually the case, not so simple. Often, companies spend a larger portion of their marketing budget on paid advertising compared to what they spend on SEO. Before we discuss why that is, let’s look at the pros and cons of the different approaches.
Benefits of SEO
- Long-term investment – Once you reach the top, you’ll keep generating free traffic as long as you keep your time optimized.
- Credibility – High rankings on Google increase your brand’s credibility.
- User-friendly – To rank highly, your website needs to be user-friendly and relevant to your visitors. That’s what you get when you work with SEO.
- High-quality traffic – In general, organic visitors convert better than paid visitors.
- Continuous growth – If you’ve done the job right, expanding your business will speed up the process of gaining positions and traffic for new keywords in the future.
- Evergreen Content – If you can create content that is continuously engaging and relevant, it will drive traffic year after year.
- Diversification – Reduces the financial risk of relying entirely on paid traffic.
- Quantifiable results – You can see the results of your investment, from improved rankings to increased traffic and ultimately increased conversions.
Disadvantages of SEO
- Time consuming – SEO takes time, coordination and expertise. To execute it correctly, you need these three elements.
- Long-term results – It often takes time for SEO efforts to pay off in the form of increased traffic.
- Algorithm updates – Google is constantly updating its algorithms, and you need to be aware of this and adapt your website accordingly.
- No guarantees – There is no guarantee of a definitive outcome in SEO.
- Larger initial investment – The labor costs of launching an SEO project are higher than PPC as it often involves more people such as developers, copywriters, etc.
Benefits of PPC
- Instant visibility – You appear in search results as soon as you press the start button and ads are approved.
- High accuracy – You can decide which keywords you want to appear on and which you don’t.
- Quantifiable results – Easy and clear measurability in terms of ROI. Clearly see which campaigns are performing well or poorly.
- Budget management – You decide how much you want to spend and on which campaigns.
- Split testing options – You can easily split test which ads are working and how – clicks, conversion rates, etc.
- Easy to customize – Campaigns can be easily customized – geographically, by season, and more.
- Flexible campaigns – Quickly and easily change and customize the text and/or appearance of ads instantly.
Disadvantages of PPC
- Escalating costs – Cost per click can quickly escalate, especially in competitive industries.
- Ongoing costs – You are only visible as long as you pay. If you turn off the campaigns, visibility disappears completely.
- Learning curve – While setting up an ad campaign is fast, it takes time to learn how to create great campaigns.
- Lower conversion rate – PPC generally has a lower conversion rate than organic traffic, resulting in wasted advertising costs.
- Lower trustworthiness – Users trust ads less than organic search results.
Is SEO or PPC best – which is better?
The disciplines may look completely opposite on the surface, but the answer isn’t simply that one is better than the other. A successful marketing strategy often encompasses both as they complement each other.
PPC can also be used to test new products, services, and ideas before investing in a long-term digital strategy.
Of course, most businesses have a long-term horizon and PPC is not enough to maximize growth and profitability. To that end, SEO is an absolute necessity.
Long-term: SEO wins, but could be supplemented by PPC
Broadly speaking, SEO is better in the long run. It creates a more sustainable and continuous flow of traffic that won’t be interrupted when you stop spending resources on it.
SEO drives relevant traffic throughout the customer journey, as strategies often include creating content for the user higher up the purchase funnel. This can be different types of guides or articles that are beneficial to people looking for information about your service. The guide you’re reading right now is one such example.
If you appear in customers’ minds from the start of the customer journey, you’ll increase both brand awareness and the chance of a subsequent conversion.
On the way to the top, and even after you’ve reached top rankings organically, it can be good to supplement with paid ads. This is especially true for searches where you don’t show up organically. You might show up in top position for “dog grooming Copenhagen”, but not at all for “dog groomer Copenhagen”. PPC is a perfect way to cover your bases.
SEO and PPC complement each other
SEO and PPC are often times perceived as binary opposites, and it’s not entirely uncommon for advocates of one to be hostile to the other. A more holistic marketing strategy includes both disciplines as they can complement each other and increase impact in the following ways:
- Dominate the search results – Being at the top of both organic and paid searches is about the most credible position you can achieve. The risk is that visitors go through the ad and you have to pay for the click, but it’s more often than not worth it
- Optimize ads and texts – Google Ads is a great way to test what texts and tone-of-voice works best and drives traffic. With this insight you can further optimize your text and its elements, such as the meta title and description. Moreover, you can better estimate whether or not your one of voice is effective in converting visitors into customers.
- Conversion insights -Use PPC to test what pages on your website converts the most visitors. This gives you an indication of which pages you should invest in search engine optimization to drive sustainable organic traffic in the long term. With this insight, you can also consider investing in PPC to attract traffic to pages that convert well. They may catch traffic from some synonyms that you don’t appear on.
- PPC can generate the initial traffic – Top rankings take time. Patience is needed when reaping the benefits of free traffic. In the meantime, PCC can be a good solution to generate traffic before the before you reach the long-term goal of your SEO efforts.
- If the algorithm changes – Google is constantly updating its algorithms. If you are negatively affected by an update, PPC can be a way to compensate for the positions you’ve lost while you update your site and win them back.
- Tough competition – In some competitive industries, it can be very difficult to rank highly and get organic rankings for important keywords. Here, you may need to use PPC to reach customers initially.
- Protect the brand – Companies often advertise on their competitors’ names as search terms. Therefore, it pays to advertise on your own brand name to protect that traffic.
What can we learn from SEO?
When working with SEO, you learn a lot about our users and what is important to them.
SEO tells you both what keywords people use when they search for your product and what they expect from your website when they land on it.
What keywords do people commonly use?
A key component of search engine optimization is understanding what people type into the search bar when they are looking for your product or service. In technical terms, these are called keywords. The more common or widespread a keyword is, the more important it is that you appear on that particular keyword.
A common mistake companies make is naming their services and products words that the average person would never use.
Example:
A British company is looking to expand to the United States. They offer vacuums, or as many Brits would say, hoovers.
As they’re planning their takeover of the American SERP, they discover a relevant keyword: cordless hoovers. Back home in the UK, there’s 13K people searching for it on a monthly basis. However, in the United States, that number drops dramatically. Why? Because an average American would never search for “Hoover” but rather a “vacuum”.
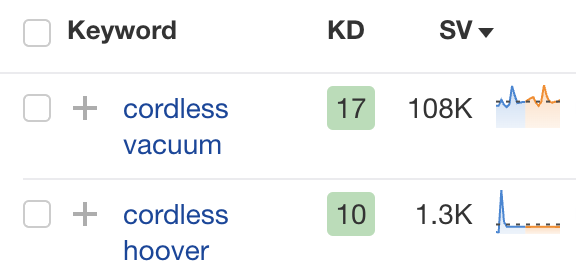
Cordless vacuum: 108K
Cordless hoover: 1.3K
If they hadn’t have done a keyword analysis, the British company could’ve missed out on a lot of potential organic traffic. Later in this guide, we will explain in-depth how to do a keyword analysis.
Which content is most user-friendly?
Companies often spend a lot of resources on customer research to understand their target audience. No matter how much time and effort you put into understanding your customers’ needs, Google can provide you with valuable insights. Their algorithm, as we mentioned before, is designed to display the most relevant results at the top!
Study the top results
Google your most important service or product and look at the top three results. How do the websites look? What is the balance between text, images, and video? What do they publish content about? How easy or difficult is it to convert through them? Try to understand what the common thread is that makes customers choose to trust them, in spite of their brand.
No matter how strong your brand is, Google won’t show you in searches if you don’t have good, user-friendly content that provides the answers to users’ search questions.
How to do it:
- Make a list of your key services and products.
- Review the top results for these keywords.
- Investigate how you can do even better than the competition
- Make it a priority to implement the changes.
- Monitor customer behavior on your pages before and after the changes.
How user-friendly is your site?
- Mobile-friendliness: The majority of Google searches are now done on smartphones, and many do not consider this when developing websites. Mobile-friendliness is often downgraded or ignored completely. This is extremely counterproductive. When Google indexes your website, they use the mobile version and ignore whether your desktop version is any good. Here you can see if your website is mobile-friendly or not: https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
- Load times: Users favor fast sites. A loading icon that spins for ages can be disastrous for your rankings. Eventually, users get bored, hit the back button, and go to a competitor instead. The risk of a bounce (a user leaving the page without interacting with it) increases by 32% between a page that loads in a single second and one that loads in three seconds.
- Accessibility: Everyone should be able to use your website, including people with different types of visual impairments. Therefore, it’s important that the text is always big enough and has sufficient contrast with the background. It’s also important that your images have descriptive metadata (alt-text) so text-to-speech and screen readers can describe to the visitor what the image represents.
Maybe you already considered it during the development of your site. Otherwise, it is about time to get started as user-friendliness is a vital part of a complete SEO process.
How do you pitch the idea of SEO at your company?
Realizing your SEO ambitions is by no means always easy. Managing SEO on your website requires time and commitment from a range of disciplines:
- SEO specialists – who do the analysis and recommendations.
- Developers – who do the technical implementations.
- Copywriters – who write user-friendly texts and ads.
- Graphic designers – who enhance the visual experience of the website.
Management may turn a blind eye because it is perceived as a large and resource-intensive project. It becomes a “nice to have” somewhere at the bottom of the priority list. So how do you get management on board?
Money talks
It’s important to highlight these gains from a successful SEO project:
- More traffic to your website.
- Better user experience.
- Increased revenue.
In most cases, the third point is the most important. Management always wants to know if the investment will pay off in monetary terms.
SEO og ROI (Return on Investment)
The absolute best way to get support for your SEO project is to be able to show with facts and figures what the profit will be if you succeed. Fortunately, you can make a solid business case yourself with our simple process.
Do your own business case
Developing an SEO business case requires different tools, both Google’s own and external. This is what you need:
Google Analytics
Google Analytics (GA) is a tool that collects data about all traffic that lands on your website, this includes:
- Where the traffic is coming from.
- How long visitors stay on the website.
- What visitors do on the website.
- Whether visitors convert.
- The value of the order placed.
Hopefully, you’ve already set up a GA account and have some form of conversion tracking in place. Using GA, you can calculate the average value of a visitor landing on a given page. If you also have an Ads campaign running, you can also draw some conclusions about the impact of keywords on conversion rate.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a similar tool to GA, but here you only see what happened prior to the visitor landing on your website. Additionally, only organic traffic is tracked. The information that can be seen in GSC is:
- Which pages visitors land on.
- Which keywords visitors have used to land on the website.
- Average position of the keyword.
- CTR (click through rate).
In the GSC, you can view data from 18 months back and examine traffic trends.
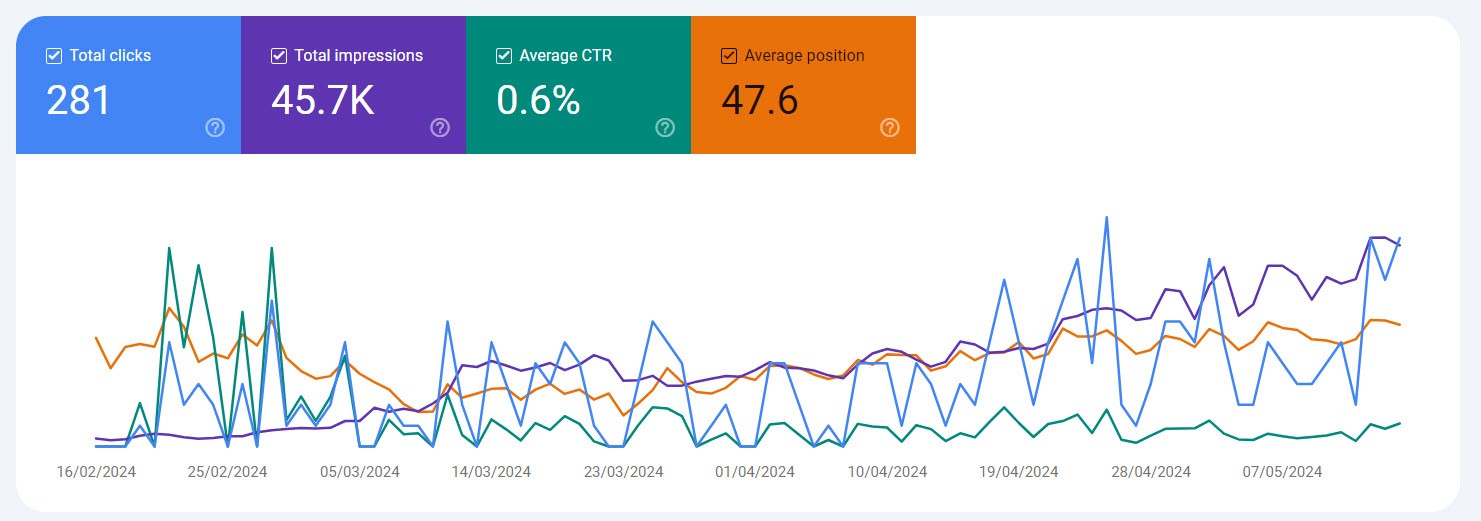
In your case, GSC acts as a tool you can use whether you’re already getting traffic on critical keywords or it’s completely dry. You may have had traffic before, but for some reason you’ve lost it.
GA and GSC give you an indication of what the situation has been like prior and what it looks like today.
Now it’s time to calculate the potential gains if you start working with SEO. To do this, you need to do a keyword analysis using a keyword tool.
Keyword research tools
There’s a vast range of tools that estimates the monthly volume of searches on a given keyword, as well as your and your competitors’ ranking on the respective keywords. We will return and dive deeper into keyword analysis later in this guide. For your business case, it’s important to list:
- The most critical keywords and their search volume
- Your current rankings on these keywords
Make your SEO business case
With insights from GA, GSC, and your keyword tool, you need to make a datasheet with the following columns:
- URL to landing page
- Keywords (Keyword tool)
- Your current ranking (Keyword tool)
- Current organic traffic on a given keyword (GSC)
- Current CTR (GSC)
- Estimated CTR (Manually estimated)
- Estimated CVR (Conversion Rate) (GA)
- The average value of orders placed
- Estimated revenue
Once you have inserted this data, it’ll be easy to estimate the gains from increased rankings on respective keywords based on the CTR-chart:
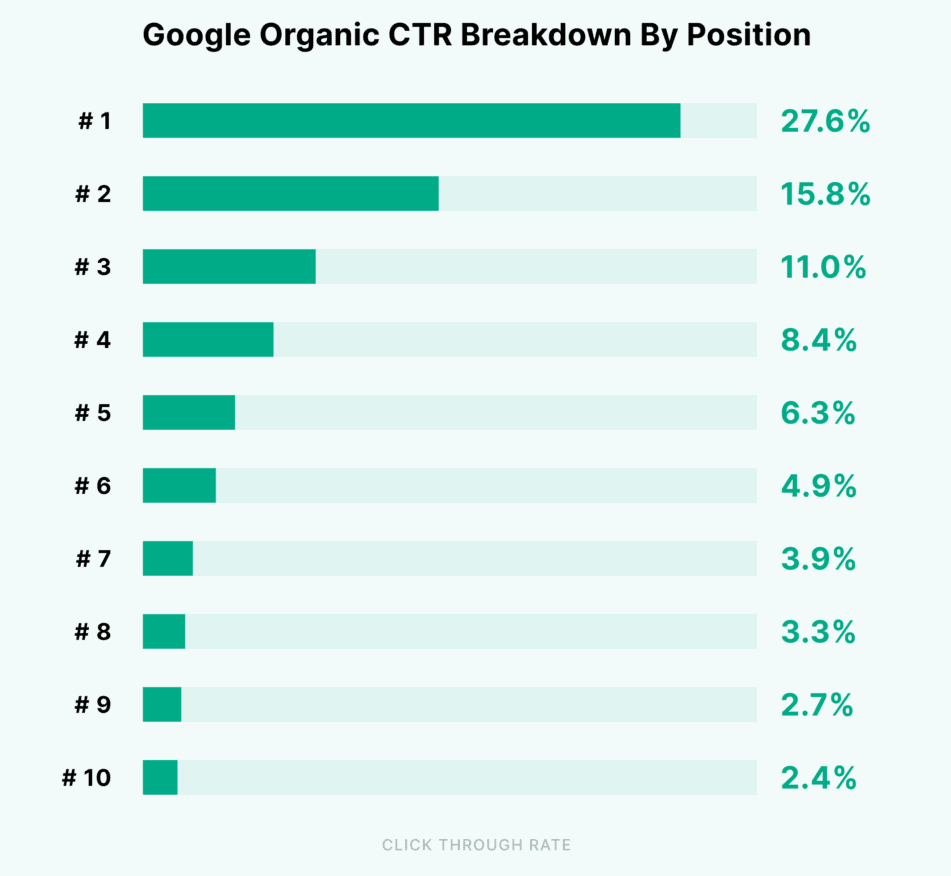
Source: Backlinko
Example:
A used car salesman in Dublin wants to generate more organic traffic from Google. The keyword “Used cars Dublin” has 2000 monthly searches.
Currently, the salesman isn’t getting any notable organic traffic. They’re curious about how much revenue a top ranking on Google with a CTR of 27.6% could generate.
Google Analytics show that 4% of all visitors are interested in purchasing a used car from the salesman. Of those, 25% complete a purchase. This translates into a conversation rate of 1% with an average order value of €20.000.

There are a number of caveats to this calculation:
-
Different industries have different average CTRs for ads and organic searches.
-
If you make it to the top rank for a given search, you will be exposed and receive traffic for related searches, such as ” used car dealers in Dublin”, “buy used car Dublin”, and so on.
-
Conversion rates can vary between paid and organic traffic.
The more data you have about your traffic and user behavior, the more accurate your calculation will be
How do you do SEO?
Now we’ve covered what SEO is all about and why it’s so important to work with it. We hope this has sparked your curiosity about what you can do to improve your ranking on Google and get more visitors.
In this final part of the guide, we will go through the different aspects of SEO, how to optimize them and how to prioritize your projects. The three areas we will cover are:
- Technical SEO – To show your website in search results, Google needs to be able to find and understand your content. Technical SEO makes this possible.It’s also about making the website user-friendly for visitors, whether they are using a desktop, smartphone, or tablet.A good technical foundation is essential to rank high on Google.
-
Content – For Google to favor your site, users need to like it too. You need relevant content, logical navigation and accessibility for people with visual impairments.
With SEO-friendly content, you get more traffic and your website converts better.
-
Off Page SEO – This is how you build your credibility through external signals. It’s about getting people and companies to vouch for you and your website through their websites and social platforms. The most important signal is backlinks.
With good Off Page SEO, you strengthen your brand and get better rankings on Google.
Below we go through the respective areas one by one.
Technical SEO
In order to display your website to its users, Google needs to find your pages (crawl) and catalog and analyze the content (index). The basis of technical SEO is to create the best conditions for this.
If the search engine can’t read or understand your content, you will never appear in search results, which will have negative consequences for traffic and revenue.
It’s not enough for Google to just understand your website. It also needs to have the technical capabilities to deliver the most user-friendly experience:
- Fast loading times. All statistics show that the faster your website loads, the more likely your visitors are to stay. Did you know that 70% of users say loading times affect their propensity to buy from an e-commerce store?
- Mobile-friendliness. It can be easy to forget when creating a website, but it’s generally more important that it looks and functions well on mobile than on desktop. As early as 2014, mobiles overtook computers as the most used type of device for browsing the web. Since fall 2020, Google has been using the mobile version of websites when crawling and indexing them.
- Security. Use HTTPS instead of HTTP. It protects visitor information and has been an important ranking factor since 2014.
- Structured data. You can let Google know what your pages contain by using structured data. For example, showing how much a product costs or how your customers have reviewed it. Google can then display this information using rich results, which increases click-through rates.
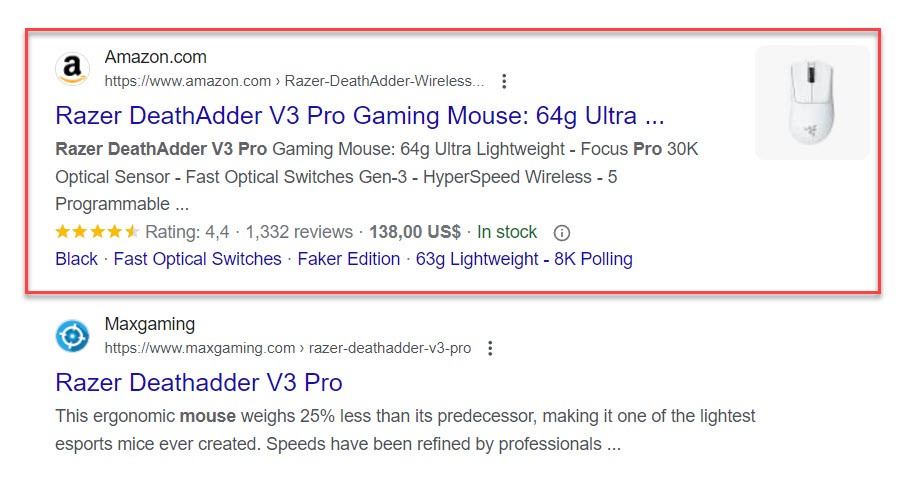
Source: Example of Rich Results
Crawling
Crawling is the term for how Google finds your pages and the basis for being seen at all.
Crawling is when Google sends its bot (also known as a spider) to your website. Once there, it reads the content and clicks on all the links it encounters.
Gradually, the bot reads the pages you’ve linked to. If they meet Google’s criteria, they are indexed and start appearing in search results.
It is crucial that the robot can find its way to the pages that you activate:
Sitemap: A file that shows all the content on your website and how Google finds it.
Internal link building: A structure of links that takes the Google bot to all the pages you want it to find.
Sitemap
The easiest way to present your pages to Google is to upload a sitemap to your website if you don’t already have one. A sitemap is a file that Google can read that shows the pages you want to index and where they can be found.
Where do I find my sitemap?
There are different ways to see if you already have a sitemap:
Enter the address of the sitemap manually
You can usually find your sitemap under the addresses
nameofwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
nameofwebsite.comsitemap_index.xml
Source: Klikkos Sitemap
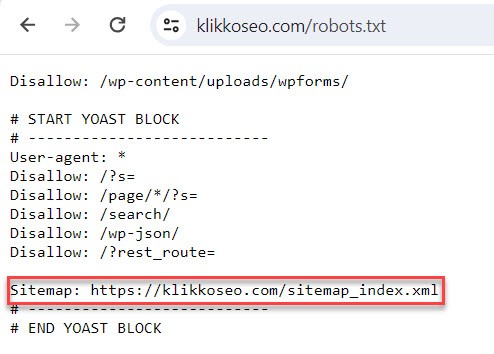
Sitemap in robots.txt
Check for the address in your robots.txt file. Robots.txt is usually found under:
yourwebsite.com/robots.txt
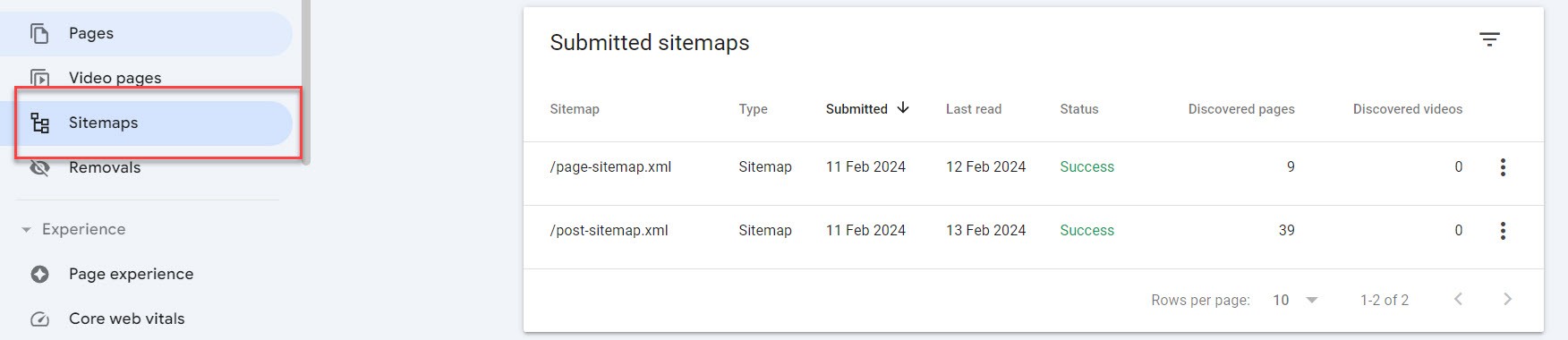
Sitemap in Google Search Console
Check out Google Search Console. In the menu you will find a link to your sitemaps if you have any uploaded.
Sitemap using Google Advanced Search Operators
Enter the following command (Google Advanced Search Operator) in the Google search box. Google will then show you whether you have an indexed sitemap:
site:yourwebsite.com filetype:xml
Sitemap in CMS
Look at the documentation in your CMS. There you can often find help on how to generate sitemaps. The procedure varies from site to site, but most websites use WordPress as their CMS and the most common plugin for generating sitemaps is Yoast SEO. You can access your sitemap by clicking on the SEO menu in the sidebar.
It’s a good idea to go in and see what your sitemap looks like once you’ve found it.
Is a sitemap necessary?
If your website is set up correctly and has a logical link structure, a sitemap is not necessary in most cases. Google will still be able to find your pages.
But it doesn’t hurt to have one, and it’s especially useful at certain times, such as when a website is brand new or if you have an e-commerce platform with millions of URLs.
If your site doesn’t have a good link structure, a sitemap helps Google find unlinked pages. However, it’s a problem you definitely want to avoid.
How do I generate a sitemap?
You can generate sitemaps in different ways. Either you or your developers can create one, but many CMSs generate sitemaps for you, either by themselves or through downloadable plugins.
Sitemaps via plugins are often dynamically updated, so when you create new URLs on your website, they are automatically added to the sitemap. There are also external websites that can generate sitemaps for you.
If you don’t have a dynamic sitemap, you’ll have to update it yourself, which can be tedious and easy to forget.
Whether you created the sitemap yourself or with the help of an external party, it’s a good idea to review it manually to make sure it’s correct.
Upload sitemap in Google Search Console
Once you’ve generated a sitemap, it’s important to upload it to Google Search Console so Google can find it. Read more here about how to upload your sitemap to GSC.
Once you have a sitemap in place, you tell Google what pages you have and where they can be found. It’s a good starting point for getting indexed and visible.
To get good rankings, a sitemap in itself is not enough. It’s more important that the search engine can easily find the pages when it crawls your website with its robot. You do this with internal linking.
Internal linkbuilding and structure
Google’s robot uses links to get around your website when it crawls it. It is therefore important that all pages can be accessed through clickable links.
If you create pages and then forget to link to them, Google’s spider will not be able to find them. This can be remedied somewhat with a sitemap, but pages that are not linked to through navigation will be downgraded by Google. It’s therefore important that your website has a clear and well thought-out link structure.
There are tools that can help you analyze your current internal linkbuilding and identify problems, such as
Crawl Depth
Crawl depth is a common term when talking about crawling. It indicates the number of clicks required to reach a specific URL from the homepage.
Google considers the earlier a page appears in the click chain, the more important it is. This means that the search engine places the most importance on pages that can be clicked on directly from the homepage. Additionally, Google believes that pages that require many clicks to reach from the homepage are not as important and therefore have a lower chance of ranking in search results.
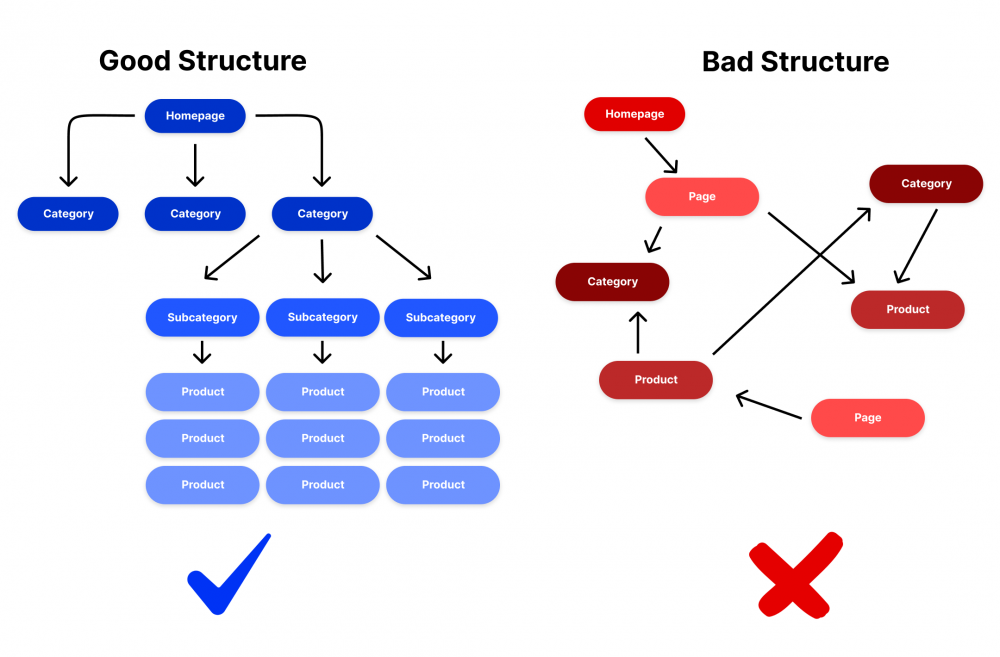
SEO-friendly website structure
An SEO-friendly structure, or architecture, is a way of organizing the content on your website in a way that makes it easy for both search engines and users to navigate.
It can look different depending on the type of website and how many URLs it contains. The general concept is that visitors starting on the homepage should be able to click through to the page that solves their problem as quickly and easily as possible.
One way to create an architecture that is friendly to both users and search engines is to categorize and subcategorize content. It’s both instructive and smart from a crawl perspective.
See the example below, which demonstrates how an online retailer can structure content for mobile phones that is friendly to both users and Google:
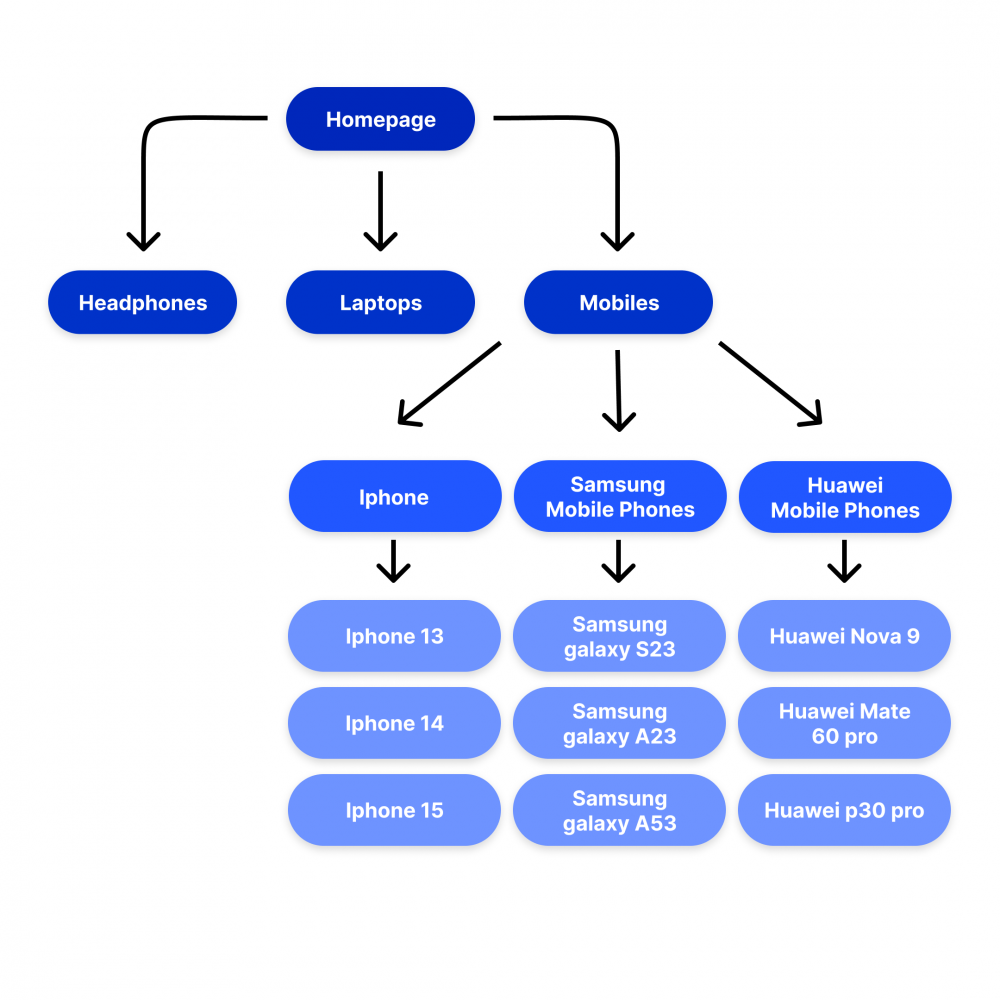
It has several positive effects:
- It’s easy and logical for users to navigate
- You get both indexable pages for category searches such as “Samsung phone”, “Huawei phone” as well as the specific products “Samsung Galaxy s23” and so on.
- You minimize crawl depth.
Indexing
Once Google has crawled your website, the search engine starts indexing your pages. This means the information on the pages is stored and analyzed to understand what types of searches they are relevant to and how they should appear in search results.
You can see if your website is indexed by typing the following command in the Google search bar:
“site:yourwebsite.com” – Google will then show the URLs on your website that are included in the index.
For example, to check if a specific URL is indexed, type the full URL after “site”:
“site:yourwebsite.com/category/product”
No Index tag
If you don’t want Google to index a specific page, you can add a “no index” tag to your pages head section. It looks like this:
Robots.txt
In your robots.txt file, you can add rules about which pages you don’t want crawlers to access. Read Google’s tutorial here on how to create and submit a robots.txt file.
Keyword
Once a page is indexed, it can start showing up in search results for the topics it describes. If this page shows up when someone searches for “Seo Guide”, for example, then we’ve certainly succeeded in our case.
To see which keywords your page is showing up for, you need an SEO tool with keyword analysis. Try using our Eye10 tool to see which keywords you are currently visible for and what rankings you have.
Loading speed and Core Web Vitals
Have you ever shut down a website in frustration because it loads for ages and nothing happens? Then you’re not alone.
The slower a page loads, the more likely a visitor is to leave without interacting in any way. In technical terms, this is called the bounce rate.
Statistics show that a page that loads in one second or faster has a 7% bounce rate, while a page that loads in five seconds has a 38% bounce rate. See the full statistics below from pingdom:
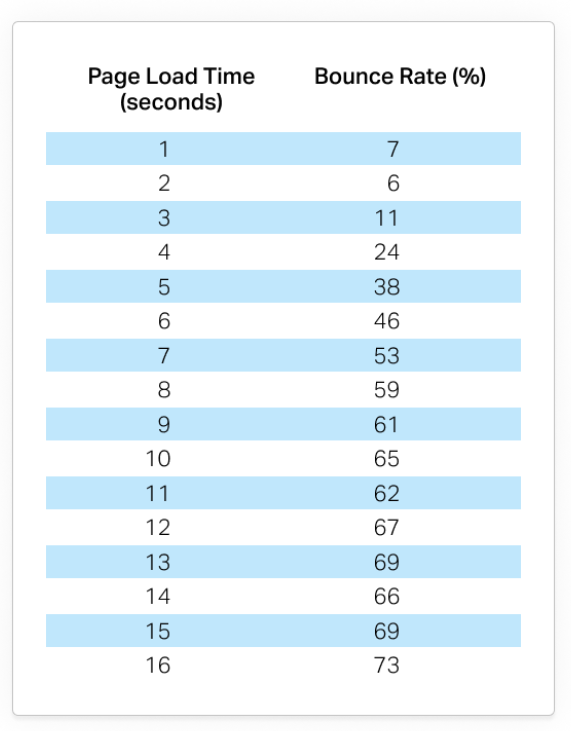
Source: Pingdom
The slower a page loads, the more likely a visitor is to leave without interacting in any way. In technical terms, this is called the bounce rate.
It’s not just the loading time itself that’s important to users. It’s also critical how the web page behaves while it loads. You may have experienced links not being clickable or things on the page moving around when an image suddenly appears. All of this affects the user’s experience of the page.
Worst case scenario, a poorly performing page can ruin all the work that has gone into building a good and usable website.
Core Web Vitals and user experience
As mentioned, Google’s goal is to showcase pages that have both the most relevant content and the best user experience.
In mid-2020, Google launched Core Web Vitals (CWV) and in June 2021 it became part of the search engine’s algorithm. CWV is a report that measures how sites are performing from a user perspective and makes recommendations for improvement.
Where do I find Core Web Vitals?
You can find the CWV report in your Google Search Console account in the menu on the left. If you haven’t already enabled Google Search Console for your website, this is another reason to do so.
How do I use Core Web Vitals?
Google has their own in-depth review of the report here: Core Web Vitals report. Below we summarize the different parts of the report and explain how you can use the insights.
CWV investigates three different areas:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – How quickly the main content of a page loads and becomes interactive. This can be both images and text.
First Input Delay (FID) – How long it takes for the website to provide some kind of response after a user has tried to use an interactive element. This could be a link or a button, for example.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Measures if and how elements are moved around the page as it loads. This can be both graphics and text, but also interactive elements like buttons or menus.
The report in Google Search Console gives you an overview of any issues. Your pages are divided into three categories: Good, Needs Improvement, and Poor. This gives you a good indication of which pages you should focus on improving.
Once you’ve identified issues, you can get more detailed recommendations for specific pages through the Google Page Speed Insights tool.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures the most critical time for the visitor; how long it takes for the main content of the page to appear and become interactive.
How do I improve the LCP?
GSC and Google Page Speed Insights give you specific tips on what to do, but general opportunities for improvement include:
- Optimized images – Make sure they are not too large and serve them in an optimized format like webp.
- Faster hosting – Better and faster hosting will naturally improve your LCP.
- Use a CDN – A stable CDN reduces the loading time of the files they serve and improves LCP.
- Lazy loading – Set up lazy loading so that images only load when a user scrolls to the image’s position on the page.
- Remove unnecessary third-party scripts – Scripts like ads, analytics, heat maps, social media, and more can significantly slow down page speed. Keep only the necessary ones.
- Optimize CSS – Reduce the size of your CSS files so they load faster.
First Input Delay (FID)
In a way, FID is a speed metric as it measures how long it takes a website to respond to what you do. For example, you might try to enter your details and submit a form or click on an interactive element.
You’ve probably clicked on something and nothing happens on the first try, only to find that it doesn’t work until later. This is obviously not user-friendly and something Google wants to counteract.
If you have a site where visitors need to be able to click and interact quickly, FID is a particularly important metric to keep an eye on.
How do I improve First Input delay (FID)?
Just like with LCP, you can measure, analyze and receive recommendations through Google Search Console and Page Speed Insights. General recommendations for improvement include:
- Minimize Javascript – Minimizing the amount of JS on the page makes it more interactive
- Split up Javascript-heavy tasks – Ask for help from your developer to do this.
- Remove unnecessary thirdparty scripts – Scripts such as ads, analyses, heat maps, social media and many other factors can significantly hamper your site’s speed. Make sure to only keep the necessary third-party scripts.
- Use the browser cache – The browser cache helps to lower the loading time of your page’s content.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS measures the stability and consistency of your page, while the content is being loaded.
You have perhaps had user experiences on websites where the site elements bounce and change size, while you’re opening the page. An ad might come out of nowhere and push the text you were reading away. These are the typical hallmarks of bad CLS, which confuses the user.
How do I improve Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
You can find both issues and solutions in the Core Web Vitals report and via Page Speed Insights. Common areas for improvement are:
- Use fixed dimensions for all media on the page – If the browser understands the size of images, videos, graphics, etc. the elements won’t resize and affect the layout when they load.
- Make sure that ad blocks have reserved space – so the content on the web page will not be moved by an ad suddenly popping up somewhere.
- Preload web fonts – to make sure the text doesn’t change when the font is loaded.
To monitor your Core Web Vitals, you can also use the Lighthouse chrome extension. It provides a broader overview of how your sites are performing and also includes metrics for SEO, accessibility, best practices and much more.
Mobile-friendly websites
Mobile phones are now the most common type of device people use to browse the internet. That’s why it’s important for Google to prioritize sites that have a good mobile experience. In fact, Google uses the mobile version of your website to crawl and index it.
Always make sure to test and monitor how the content looks on mobile before you launch something.
How do I know if my page is mobile-friendly
Google has developed a tool that shows whether your website is mobile friendly or not. You can test your website with Google’s Mobile Friendliness Test.
You can also see how mobile friendly your website is via Google Search Console. Go to the “Mobile Usability” section. There you can also see what issues, if any, you should fix.
Security and HTTPS
To make it clear and simple, you should switch to HTTPS, if you haven’t already done so.
HTTPS makes your website more secure for users and is an important ranking factor in Google’s eyes. In addition, Google displays warnings to visitors if your site is not using HTTPS.
Structured data and rich results
By helping Google understand the content on your website, the search engine can create more valuable and user-friendly search results. In technical terms, these are called Rich Results.
One of the best ways to get Rich Results is to use structured data.
What is structured data?
Structured data is a way of using standardized formats, such as JSON-LD, to tell search engines exactly what an element on the website is. Examples of common types of structured data are:
- Product information (pictures, price, offers…)
- Contact information (company name, address, opening hours…)
- Recipes (ingredients, nutritional value, time to prepare…)
- Reviews (Ratings, written reviews…)
Why should I use structured data?
If you properly mark your website content with structured data, you can get richer search results, Rich Results, which show both reviews and prices. Here’s an example:
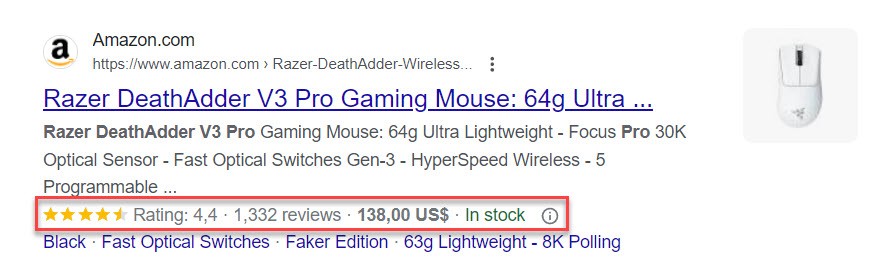
Rich Results provides better CTR and more traffic to your website. Nestlé reported that they increased their CTR by 82% on their pages with Rich Results.
How do I create structured data?
If you’re interested in learning more about structured data and how to implement it, Google has great resources that you can check out.
Technical SEO analysis
A technical SEO analysis identifies problems and shows you how you can improve your website. We’ve already covered some of the key areas above, but a technical SEO analysis also covers…
- Indexing issues – When pages that should be indexed aren’t
- Duplicate content issues – If you have duplicate content on more than one URL. This is rated negatively by Google.
- Status codes – Responses from web servers showing the status of a website. They indicate whether the page is loaded correctly (2XX), if errors occurred (4XX for customer error, 5XX for server error) or is being redirected (3XX).
- Internationalization – Whether international versions of the website are set up correctly (Hreflang).
Unfortunately, we don’t have scope in this guide to cover all the facets of technical SEO. But if you want to do a thorough technical SEO analysis, there are some great tools available in addition to Google Search Console:
Screaming Frog – Perfect for smaller websites
Semrush – Better for larger sites and agencies
Ahrefs – Both technical and content audit
Content
Once your technical foundation is set up, it’s time to make sure search engines and users love the content on your website.
We will cover the following areas that you should be familiar with:
- Keyword analysis
- Keyword optimizing content
- Metadata – Titles and descriptions
- H1 title and subtitles
- URL slug
- Images
- Body text
- Relevant content
- Internal linking
A common thread throughout this part of the guide is that you need to have an outside-in approach. Put yourself in the customer’s shoes. That’s where it all starts.
Keyword analysis
First, you need to gain an understanding of what your target audience types into the search bar when they are looking for your content. In technical terms, these are called keywords.
It’s not uncommon for companies and organizations to name their products and services by using words that ordinary people would never use. If you do this, no one is likely to find you.
To find the right keywords, there are a number of tools available online. Most of them measure the following important metrics:
- Search volume – How many times a month a given keyword is searched.
- Your rankings – How your website positions on different keywords.
- Competitors – Which competitors rank for the keywords you are interested in.
- Difficulty – How easy or difficult it will be to rank for a keyword.
Commonly used keyword tools include:
In addition to these, you can use Google’s own tools to gain insight into keywords:
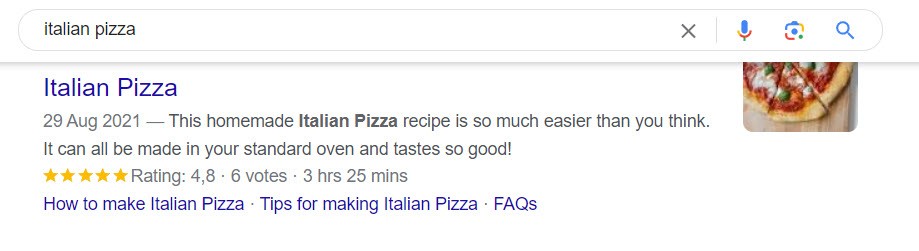
It’s also important to understand the intent behind each keyword. Maybe your restaurant makes the best Italian pizza in town. A search for “Italian pizza” will return the most recipes, while a search for “Italian pizzeria” will return more relevant results if you are a restaurant.
A keyword analysis is usually performed by doing the following:
- Make a list of services and products – Make a list of all the products and services you consider important to your business in a document, such as an Excel or Word sheet. If possible, rank them according to what provides the most business value for you. Also, write down the pages which should be visible for that particular service/product.
- Analysis, current keywords – Use the tools to find out which keywords you are currently ranking on and which pages the keywords appear on.
- Analysis, potential keywords – Check if there are more common or widely used keywords for your services/products than the ones you currently rank on.
- Competitor analysis – Get an overview of the competitors who are ranked at the top for the relevant keywords and who tend to rank on synonyms and other valuable related searches. A competitor analysis also shows how difficult or easy it will be for you to get to the top.
- Collect data and prioritize – You should now have a good picture of the landscape and your potential. This is the forms basis for what you should going forward. Often it makes sense to go for the keywords that have the biggest impact with the least effort.
Once you have your prioritized list, it’s time to start optimizing your content for keywords.
Keyword optimization
Keyword optimization is all about getting Google to show your website at the top of the search results for your most important keywords. You achieve this by inserting the keyword in the right places within the content and delivering the most user-friendly experience.
Meta data – titles and descriptions
The Google search result is where your user first encounters you. The result consists of different components, of which Meta Title and Meta Description influence your keyword optimization, albeit in slightly different ways.
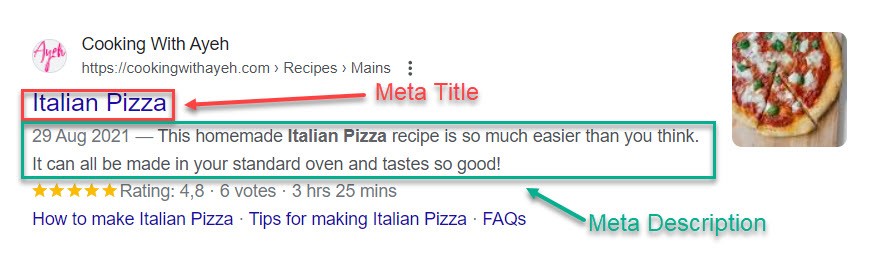
Meta Title is, as the word suggests, the title of the page in the search engines. Google pays a lot of attention to the words you choose for it, as the meta title indicates the main topic of the page. It is a direct ranking factor. Best practice is to include the most important keyword early in the title, preferably first.
The meta title can be different from the title (H1) you display when a visitor lands on the page, but it makes sense that they are relatively similar for user-friendliness purposes.
The ideal length for a meta title is 50-60 characters, including spaces. It shouldn’t be too long as it risks being cut off mid-text in the result. Use a tool like To The Web’s length checker to see if your title is within the limits.
Meta description
The Meta Description is a chunk of text appearing below the meta title, which describes in further detail what the page is about. It has no direct impact on your page’s ranking in search results. But a well-written description can attract clicks and a high CTR (click-through rate) is a ranking factor.
Unfortunately, there is no guarantee that Google display syour provided meta description. The search engine can sometimes take sections from the page’s text content and display them instead.
Since your keywords are bolded in the search results, make sure to include them in the description to provide a clearer user experience.
H1 and sub-headings
H1 is the main title of the page itself. It should be the same or similar to the one you use as the meta title. There is no maximum length requirments for H1, so you can certainly go over the aforementioned character limit here. The main keyword is the most important element on the page, as it describes the content of the page. Accordingly, it must be included in the main title.
Feel free to use the main keyword and synonyms in the rest of the page headers (H2-H5), but focus on user-friendliness. If it’s obvious to the user that you’re overusing a keyword, it will most likely be obvious to Google as well. Keyword stuffing, as it is called in the industry, can negatively affect your ranking.
URL slug
The URL slug is the part of a site address, which is specific to a particular page.
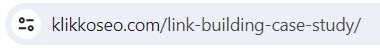
The slug should be simple and descriptive, but not too long. Usually the slug is automatically set based on the page title, but feel free to shorten it if it’s too long. You can also consider…:
- Being consistent in how spaces are defined. Preferably use hyphens like this: /seo-guide/
- Not using years in the slug, if the content is planned for long-term use:
– /seo-guide-2023/ – Bad
– /seo-guide/ – Good
We want to rank on “SEO guide” every year. If we create a new page every year, the ranking will be set back to 0 on each new iteration. It’s sufficient to include the year in the title heading.
- Make sure to redirect the old URL to the new one, if you change the URL.
Images
Google is currently unable to read images, but you can indicate what the image is about in its alt text. An alt text is the text that appears if an image doesn’t load in the browser. It is also read aloud to visually impaired users who use screen readers to help them navigate.
Since it helps the search engine contextualize the content of the page, it is a ranking factor for Google. Make your keywords appear naturally in image alt-texts, so they are useful for both visually impaired users and Google.
Optimized alt texts might also feature in Google’s image search, which can be an additional source of traffic.
Body text
Make sure to naturally include the keyword in the page’s body text. Feel free to use synonyms and paraphrases, but keep the focus on the user. The text should not feel contrived or difficult to read. Keyword stuffing has a negative effect for Google and users alike.
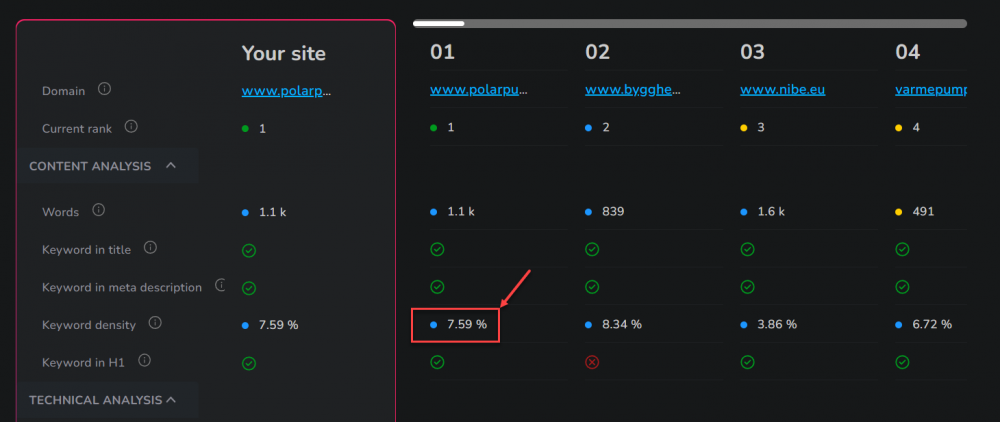
Keyword in density in Eye10
Relevant content
We have mentioned it a few times, but it’s always worth repeating: Google wants to display the most relevant content at the top of the rankings. The exact implication of this differs based on the particular search.
You can get a good grasp of relevance by Googling your keyword and analyzing the top results. Do they have a lot of visual content? Videos? How user-friendly are they? You’ll also want to know how many words it takes to beat your competitors. A complete guide on a topic like the one you’re reading now requires thousands of words in order to be comprehensive and relevant:
- The top page on the keyword “SEO” currently has 5400 words.
- Meanwhile, the top page on the keyword “oled tv” has just 112 words at the moment.
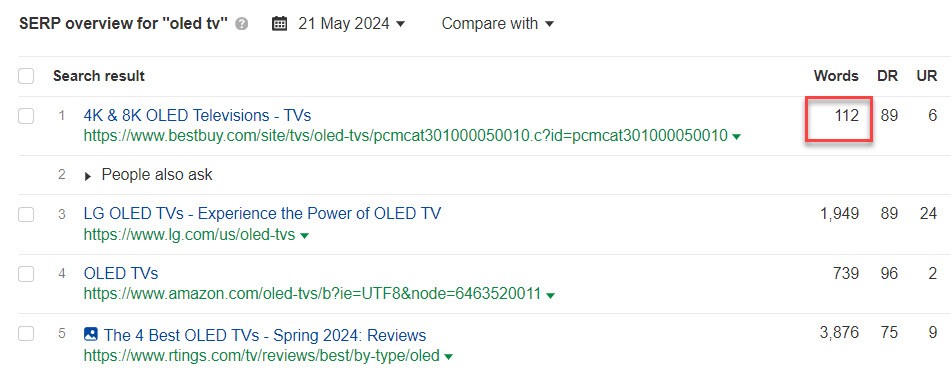
Source: Ahrefs
Creating content that is as user-friendly and relevant as possible is important for two reasons:
- Your site will improve its engagement and conversion rates
- When determining page ranking, Google considers user behavior. It’s a positive ranking signal if users click through your site and interact with it. If they go straight back to the search results, it’s considered a bounce, which is a bad signal.
Internal linking
Internal linking is a means of directing users to other pages on your website. It can be links via written content, images and menus. Well thought-out internal linking is both user-friendly and good for your SEO.
For example, if we had an in-depth guide to “internal linking”, we could link to it in this chapter. Ideally, you would make it easy for users to reach the in-depth resources they are looking for. You’ve probably been in situations where you’re stuck on a page and don’t know how to move forward. Avoid creating those situations for your users at all costs.
Anchor texts
It’s important to use the keyword of the page being referred to in the anchor text (the SEO term for the hyperlinked part of the text). This contextualizes the content of the page from Google’s perspective.
Navigation
Imagine you are a user who has never visited your website before and you land on your homepage. How easy is it for the user to navigate the page? Is it clear to them what they should do?
Make it as easy and clear as possible for the user to navigate to your most important pages and make sure the links leading to your pages use the keywords as anchor texts.
Also, make sure that Google can follow the links. This means that they should also be accessible in the site’s mobile version, as Google uses it for crawling and indexing. More on this below.
Off-page SEO
When people think of search engine optimization (SEO), they tend to imagine tweaking the content on their website or improving the technical side of their website towards faster load times or mobile optimization. While these on-page elements are crucial, there is another side of the SEO coin that is often overlooked: off-page SEO.
Off-page SEO refers to activities outside your own website, which affect your site’s ranking in search engine results. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Link Building
- E-E-A-T
- Brand Building
- Content Marketing
The core of off-page SEO is about establishing authority, trust and relevance for your website through external sources.
Improving your site’s credibility: Master E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T is short for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness.
The concept was first introduced in 2014 under the name E-A-T – initially without the inclusion of Experience. It is an important part of Google’s Quality Rater’s Guidelines, which are guidelines for Google employees who manually review websites. The extra E was added in 2022.
E-E-A-T is a means of assessing the credibility of websites as sources of information. It is especially important for sites which may affect a user’s health, finances or well-being – these are often called “YMYL” (Your Money or Your Life) sites.
Experience: The author of the content should have experience regarding the topic they are writing about. It will boost your credibility, if you can prove that you have tested and practiced the advice you provide.
Expertise: Experience focuses on the content on the page. Is the text written by an expert or enthusiast who knows the topic well? In medical topics, content written by doctors or healthcare professionals is considered relevant. On the other hand, medical advice from lay people can be downright dangerous.
Authoritativeness: This part focuses on both the content and the author. Is the author recognized in their field? Is the website known as an authority in its field?
Trustworthiness: Is the information on the website reliable? This applies to the content and the technical security of the website equally. For example, a page asking for personal information should use a secure connection (HTTPS).
It’s important to note that E-E-A-T is not a direct ranking factor, but an indication of how Google wants their algorithms to work.
Brand building
Strong brands and figureheads are not just good for how the public perceives your business. It also provides greater organic reach on Google.
It sends a positive signal to Google, when your company or a leading figure is presented as an expert on a topic. This tells the search engine that it’s relevant and safe to feature your content on that topic.
This is not much different from how humans function. The more a company or individual communicates credibly on a topic, the higher their reputation is in the eyes of the public.
Brand building, SEO, and businesses
By building your brand and becoming an authority in your field, you’ll get higher rankings and more traffic on Google.
How it works
Google can tell when your business is mentioned on other websites. The more credible the website and the more positive and relevant the context, the better.
Examples:
If for some reason Tesla were to recommend a small electric car dealer in Akron, the car dealer’s website would get a huge boost on searches like “electric cars in Ohio”, “electric cars in Akron” etc.
Brand Building, SEO and individuals
If you as an individual build authority in Google’s eyes, content where you are featured will be interpreted as more relevant. The end result is more traffic to the page where the content is published.
The more traffic and attention your content gets, the higher the authority. This ultimately has a self-perpetuating effect.
It’s a good idea for your company to have one or more leading figures who are experts in the field and who can be public-facing on your company’s behalf.
The Covid pandemic serves as another example, where a number of experts appeared in the media time and time again to explain concepts, participate in debates and update the public.
Here’s a graph from Google’s Trends tool (showing relative search interest in topics over time) for “Anthony Fauci”. Note the large spike in March 2020, when the epidemic first broke out in the US.
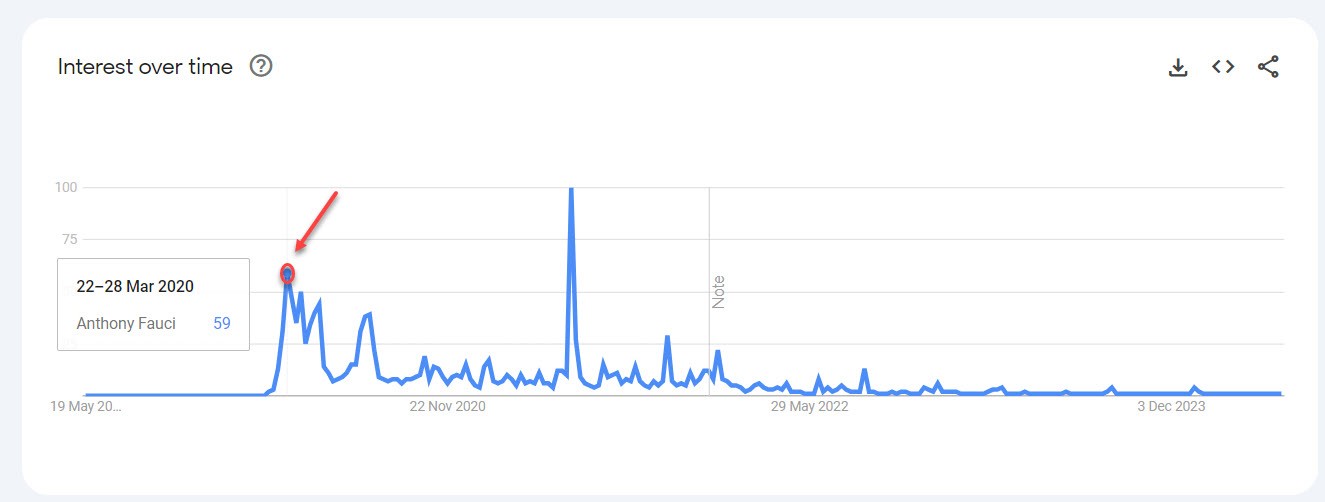
Although not everyone necessarily liked him, he became an authority in the eyes of many people – and also in the eyes of Google. Every time he featured as an expert voice, his relevance to the search engine increased.
An article about Covid featuring Anthony Fauci has a good chance of appearing among the top results on Google. If the article was written by a researcher unknown to Google, Google would not show it. If Fauci instead wrote an article about SEO, Google wouldn’t care either.
Let’s do a thought experiment. Imagine you want to know what the status of COVID-19 is right now and you Google “COVID-19 recommendations today”. If you see a random blog at the top of the search results followed by the CDC website below, which one would you click on? Which one would you trust the most?
Even if it’s not at the top of search results, a strong and credible brand can drive more traffic.
How do you work on branding and SEO?
Working on branding and SEO is a large and complex task which includes:
- Brand definition – What are your USPs (Unique Selling Point), goals and values? Make sure your message matches the needs of your target audience.
- Consistent branding – Make sure your message, graphic profile and tone of voice are consistent across online platforms: websites, social media, ads, etc.
- High-quality content – Produce content people want to interact with, share and talk about. Ideally, you would have data and insights nobody else has. Read more about this in the next chapter on Content Marketing.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is about creating content which resonates with a target audience and promoting it in the target audience’s channels. This could be articles, videos, whitepapers, guides, different types of tools, etc.
Content marketing can have different purposes, including:
- Increase brand awareness – The more often your target audience sees the content (and ideally interacts with it), the more familiar and aware they become of your brand
- Attract new customers – A common goal of content marketing campaigns is to drive leads and conversions
- Build credibility – By providing reliable information and education on your area of expertise, you build credibility with customers (and Google)
- Retain customers – By continuously providing value for old and existing customers, you build long-lasting and close relationships
- SEO – By creating valuable content for others to reference, such as data and statistics, you can improve your SEO through the links you receive.
SEO-based Content Marketing
Content Marketing can have different purposes. Since this is an SEO guide, we will focus on how to do Content Marketing which improves your website’s ranking on Google.
The key is to create content people want to refer and link to. They might want to do it because it’s funny, informative, thought-provoking, useful or any other reason.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for all industries and businesses. You need to adapt your strategy to what you’re able to produce and what your target audience might be interested in.
The cost of SEO content marketing varies greatly depending on what you want to do and whether you use an agency or do it yourself.
Four budget-friendly content-marketing strategies
- Case studies – Industry-related case studies are a safe bet if the context is relevant and the study is well executed. Consider for example how many external studies we refer to in this guide.
- Provide expert opinions – If you or someone else in your company is an expert in a certain area, use that to your advantage. Use HARO (help a reporter out) or network with journalists who write about your topic. This strengthens both your SEO and the authority of the expert.
- Own interviews – Conduct your own interviews if your platform allows it. Invite external experts to share their best tips with you. At the very least, you’ll probably get a link from the experts’ own platforms.
- Comprehensive guides – Find out what the most common problems are in your industry and create the best guides to tackle them. You’ve probably recommended a really good guide to a friend at some point. Let that feeling inspire you.
Strategies for slightly bigger budgets
If you have the money and the resources, there are other strategies you can consider. For instance, you can:
- Use a tool – There is something of interest to measure, analyze or calculate in every industry. For example, electricity consumption when switching to solar panels or calorie consumption when exercising. In our case, we have the Eye10 tool, whose free features are useful for many people out there. Think about whether you fill a gap or a need in your industry by developing a tool or a calculator.
- Hire an agency – There are many agencies out there who are experts in creating campaigns towards brand building and SEO. Take a look at their previous campaigns and ask to see the results before you decide.
- Conduct a research study – An industry-related research study with a relevant angle can be a great way to generate attention, publicity and links. Maybe you can even collaborate with a local university?
Link building in SEO: Why links are essential
Link building is the process of getting inbound links from other websites to your own. These links, often called ‘backlinks’, act as bridges between different pages on the internet and play a central role in the SEO landscape. But why are they so important?
A seal of approval for search engines: Search engines like Google consider backlinks a kind of recommendation from one website to another. If a high-authority website links to your site, search engines consider it a sign that your content is valuable, trustworthy and relevant.
Each link serves as a recommendation or vote of confidence. The more quality links a website has, the more authoritative and trustworthy it appears in the eyes of search engines.
Authority and relevance: A strong link profile (i.e. many quality links from credible sources) helps establish your website as an authority in your field. Authoritative websites often rank higher in search results as they are considered more trustworthy.
Web traffic: Besides improving your SEO ranking, high-quality backlinks can also drive direct traffic to your website. If a user is reading a post on another website and sees a link to your website, they can click on it and be introduced to your content.
Indexing: Search engines use “crawlers” or “bots” to crawl and index websites. Backlinks help these crawlers find your website and index it faster.
Competitive advantage: In competitive industries where many websites compete for the same keywords, a strong link profile can give your site an edge.
In SEO, link building is like getting personal recommendations for your website. It’s a way of telling search engines and users that your content is not only relevant, but also trusted by others on the internet.
In a digital landscape where visibility is a key factor for success, link building is an indispensable tactic to ensure your website is not only seen, but also valued and ranked highly. You can read more about link building here.
The importance of a well-defined SEO strategy
Without a well-defined strategy, any project, regardless of scope, can easily become a detour riddled with guesswork and ineffective decisions. This is especially true for SEO, where results can often take time and require careful navigation through ever-changing algorithms.
That’s why it’s crucial to start with a clear goal. This provides a clear direction and a concrete vision of what success would look like.
Next, it’s important to set a realistic budget to ensure you have the necessary resources to execute the plan and achieve your goals without running into financial issues.
Finally, it’s important to define how you will measure success. Without clear benchmarks for success, you may end up fumbling in the dark without knowing if your areas of focus are really creating value.
Launching an SEO strategy requires time, patience and constant learning. But with a dedicated effort, you can increase your website’s visibility, traffic and ultimately – conversion rates.
Navigating towards online success: The art of setting dynamic SEO goals
Defining clear SEO goals is the foundation of any successful online strategy. Imagine embarking on a journey without having a specific destination in mind; you would wander aimlessly and waste precious time and resources.
Without clear SEO goals, you may end up implementing things without understanding their true value or impact.
With a clear goal, you can focus your efforts on what really makes an impact. Common goals for SEO projects include:
- Improved organic rankings
- Increased organic traffic
- More qualitative leads
- Higher conversion rates
- Building brand awareness
- Geographical expansion
- Sustainable growth
Each of these goals requires its own approach and different tools and techniques.
When you know what you’re aiming for, you are better positioned to allocate resources, adjust your strategy based on data and make sure everyone involved is focused on the same primary goal.
Here are some tips on how to effectively define and implement your SEO goals:
SMART goals: Make sure your goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
Understand your business needs: SEO should support your overall business strategy. Do you need to increase brand awareness, sales, leads or something else entirely?
Baseline data: Before you can set a goal, you need to know your current baseline. Check your current traffic, rankings, conversion rates and other important metrics.
Competitor analysis: See how your competitors rank and what kind of traffic they receive. This can provide insights into potential opportunities and challenges.
Segmentation: Break down your goals based on different segments such as organic searches, referral traffic, geography, etc.
Be realistic: While it’s good to aim high, your goals should still be achievable based on your effort, budget and market situation.
Focus on quality: It’s not always about quantity. Focusing on quality traffic that converts better can often be more valuable than simple volume.
Think beyond rankings: While rankings are important, they are not the only indicator of SEO success. Consider user experience, page load time and other technical aspects.
Feedback loop: Ensure regular monitoring and reporting. This allows you to adjust your strategy based on the results you measure.
Team commitment: Make sure all relevant team members (from copywriters to technical staff) are aware of and working towards the same SEO goals.
Continuous learning: The SEO landscape is constantly changing. Be prepared to adapt your goals in response to industry changes, algorithm updates or new business needs.
By following these tips, you can create clear and focused SEO goals, which guide your team and your efforts towards measurable success.
Does your SEO budget match your ambitions?
A well-executed SEO strategy can be the difference between flourishing online or disappearing into the crowd. However, as with any investment, it’s not just about spending money, but spending it wisely.
A well-considered SEO budget ensures that you can allocate resources exactly where they will have the greatest impact. By setting a budget, you not only signal big ambitions, but also that your understand of how real growth requires strategic planning and investment.
In order to create a sensible budget, you need to have an understanding of…:
- Your goals
- Your preconditions: current traffic, positions, conversion rate, etc.
- The resources/funds the project requires
- How you prioritize between the proposed projects
- That SEO takes time and will not show immediate results.
As you can probably tell, there’s a lot to take into account when creating the foundations for an SEO budget. If this all feels overwhelming, an SEO agency or consultant can help you with documentation, analysis and prioritization suggestions.
Measuring the real impact of SEO
Measuring SEO success isn’t just about looking at a single number or the search engine ranking; it’s an art combining data, intuition and business sense.
Most people without SEO knowledge can’t see the forest for tress by focusing excessively on page 1 ranking. On the other hand, SEO specialists dive into analytics tools which closely analyze:
- The quality of traffic
- User behavior
- Conversion rates
- Evolving trends
- … and much more
Every click can be the start of a new customer journey. That’s why understanding and measuring SEO success is key to building lasting relationships and achieving a commanding market position. Measuring SEO success isn’t just a technical discipline – it’s the heart of your digital strategy.
If you’re ready to take your SEO journey to the next level and kickstart your growth, we’re ready to guide you every step of the way.
FAQ
What does SEO cost?
What does SEO include?
Technical SEO covers the technical aspect of optimizing your website to cater to the algorithms. It deals with assisting the search engines find and index your site, creating a user-friendly experience focusing on decreasing load time, mobile-friendliness, and more. Content is all about creating content that answers users’ questions in the most efficient way. Off-page considers all external activities. It is mostly centered around acquiring links that link to your website, which increases your sites credibility in the eyes of the algorithm, positioning your site as a trustworthy source for your audience and bettering your rank.



