Backlinks are one of the most important ranking factors for Google. They act as quality markers and increase the authority of a website in the eyes of search engines. This ultimately leads to better rankings and more traffic for a website.
Getting good backlinks is the most difficult and controversial area in SEO. On the one hand, there are the ‘ethical’ techniques, White Hat SEO, which slavishly follows Google’s guidelines. On the other hand, there is Black Hat SEO – techniques that bypass Google’s rules and recommendations.
In this guide, you will learn about the different techniques and how to implement a backlink strategy yourself. We have also conducted the largest case study in the Nordic region on how different link building techniques actually deliver. More about that below.
Table of Contents
What are Backlinks?
Backlinks are what we call a website linking to another website. It can look like a few different ways:
Link with anchor text – Link embedded in a descriptive text, like this one:
Exact URL – Link via the exact UR that leads to the landing page, like this: https://searchroyals.com/
Link via image – Link embedded in an image or graphic, so that the image is clickable, like the example below:

Why do you need backlinks?
Backlinks are important for various reasons:
- Improved positions in search results. Quality links are positive signals in the search engines’ algorithms. That is, they give websites better positions in the search results.
- Increased traffic. A backlink from a well-visited page can generate traffic to your site.
- Branding. If your website appears as a source of data, knowledge or expertise, the perception of your brand improves.
When working with SEO and backlinks, the main goal is to improve your position on Google. Better positions mean more traffic. See the graph below from Backlinko that shows the percentage of clicks that different positions receive from Google:
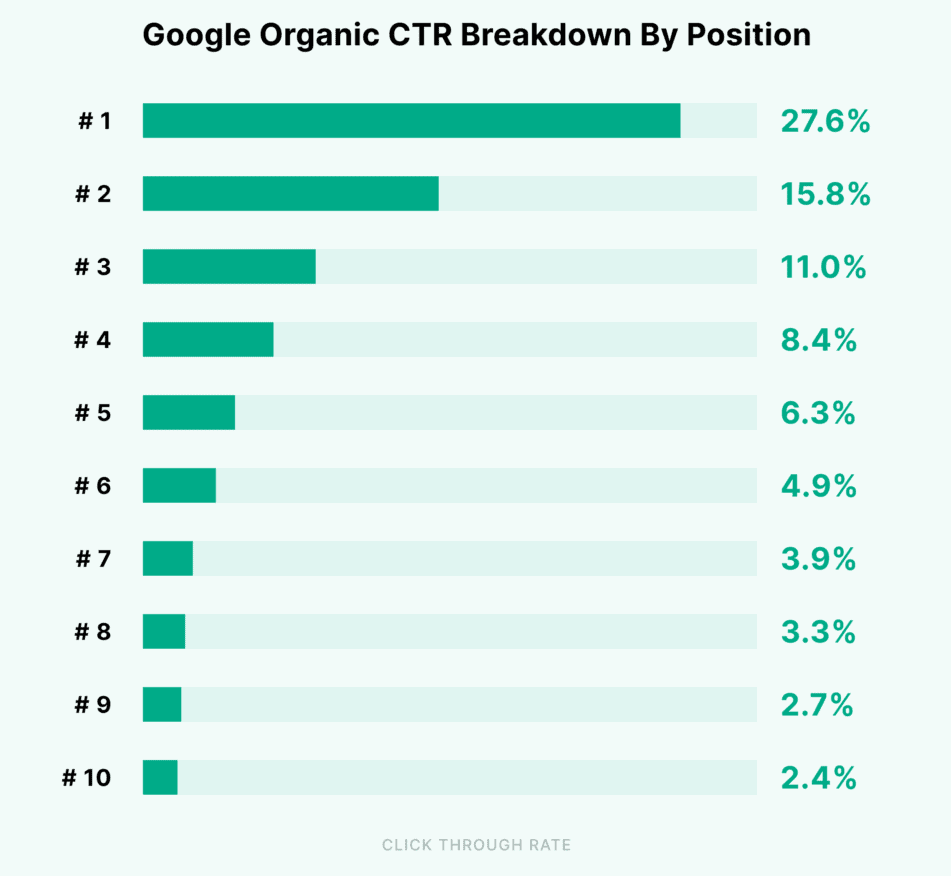
The top three positions receive more than half of the traffic. Reaching the top generally requires a strong link profile. By link profile we mean the quality, quantity and relevance of the links pointing to your site.
Which backlinks are good for SEO?
Not all links are created equal. There are three crucial factors:
1. Dofollow/nofollow – Links can be labelled with a meta tag that tells the search engines not to bother with it. The most common is the “nofollow” tag, but “sponsored” (paid links) and “ugc” (user-generated content) also tell Google not to give links any value.
The links that do not have any of these meta tags are called dofollow links, even though no such meta tag actually exists. It’s the dofollow links we want.
To see if a link has a meta tag, you can right-click on the link and select “inspect”. See an example of a nofollow link below:

2. Link quality – Generally speaking, the stronger the page that links to you, the better it is for your site. On the other hand, a link from a dodgy page can be downright damaging and lower your position.
3. Link relevance – It is important to Google that the content of the page the links are on is relevant to the content of your page. If you sell furniture and get a link from a page about hockey, there is no natural common ground. Google sees and understands this.
How does link strength work?
Link strength, or link juice, is an arbitrary measure of how much SEO power a link gives to the receiving site. The stronger the site sending the link, the more link juice. The prevailing theory is that link strength is a positive ranking signal with search engines.
There are a number of tools that measure the strength of your site and others’ sites:
When a link points to a page, it sends a certain amount of link juice, depending on the strength of the sender’s page. Most of it stays on the receiving URL and the rest is distributed further on the site, through the page’s internal links.
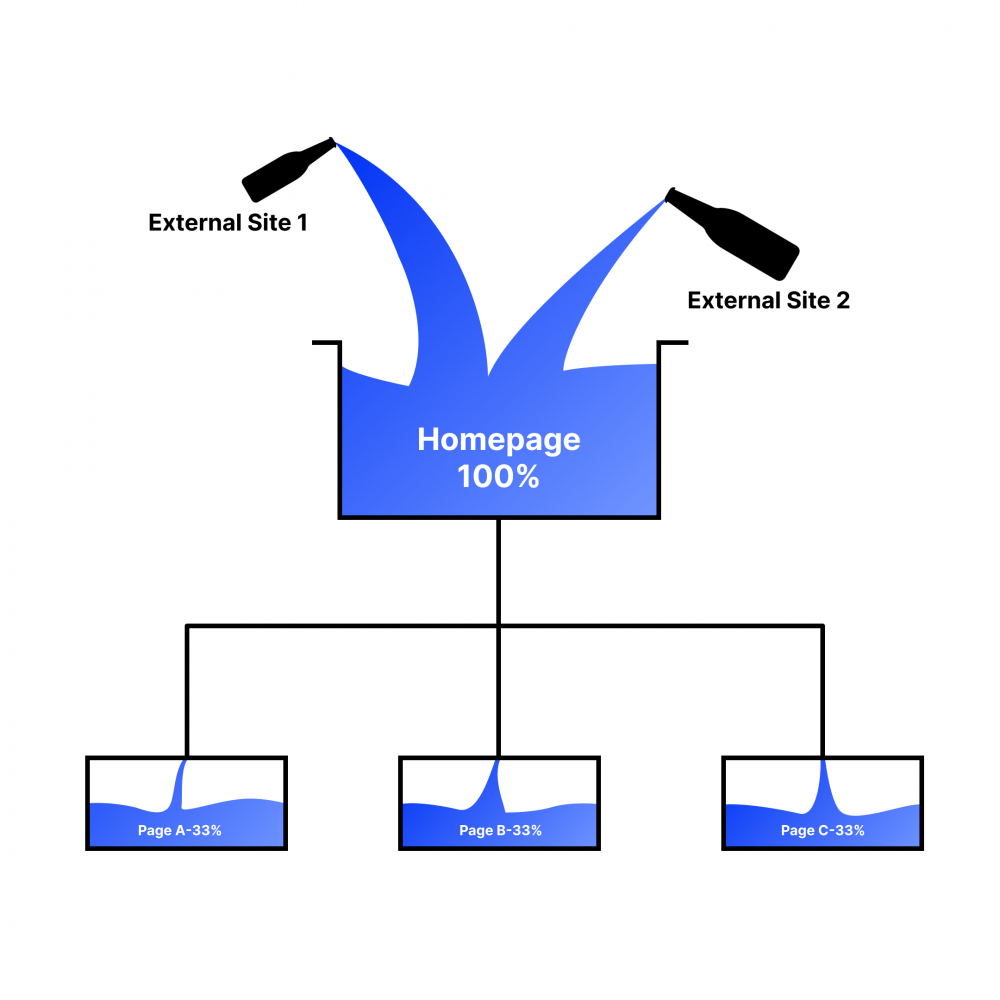
The homepage is the strongest
Backlinks often point to your homepage, making it the strongest page. It also means that your home page is generally the page that is best suited to appear for your main keyword. See examples below of search results for “law firm Stockholm”. All the pages shown below are the websites’ home pages:
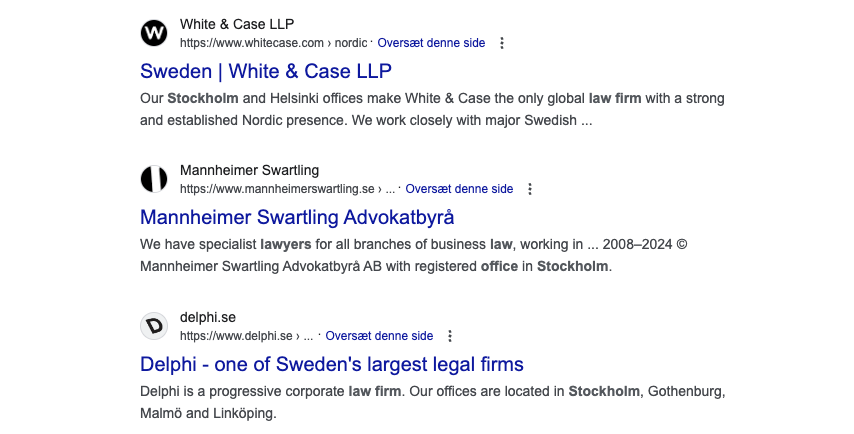
Link strength to subpages
It is important that you get backlinks to all pages that are critical to your business, not just the homepage. This gives them a greater chance of appearing in Google’s search results for relevant searches.
If you have an online shop, it is important that you are visible on the products you sell, both in terms of product names and categories. Here is an example from the search “Buy TV” with 2200 searches per month (Data from Ahrefs).
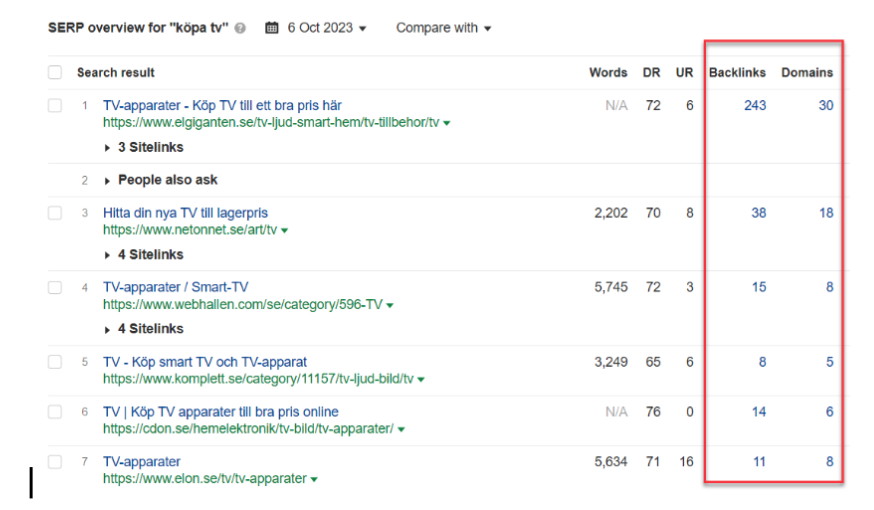
Elgiganten, which ranks at position 1 has 243 backlinks from 30 unique domains while Netonnet at position 2 has only 38 links from 18 unique domains.
Even if your homepage sends some of its link strength to product/service pages, it is important that they get their own relevant links.
What is link building?
Link building are techniques that you can use to get backlinks to your website. It often involves:
- Purchased links – Paying for the links you want.
- Content Marketing – Creating content that attracts links and engagement.
- Outreach – Actively seeking out websites that can link to you.
- PR – Marketing relevant content to journalists and media.
What is the difference between Black Hat and White Hat?
Google has set up guidelines for what types of linking activities are considered unauthorised under their Spam Policies. It is mainly their Link Spam that is relevant to this discussion. It says, among other things, that the following is not allowed:
- Paying for links or posts containing links. This includes payment with money, services or goods.
- Excessive link exchanges, i.e. your site and the other site linking back and forth between each other in an unnatural way.
- Requiring a dofollow link as part of an agreement.
- Different types of promotional links that are not labelled with meta-tags that block link strength (nofollow/sponsored).
- Pages with too many links pointing to you, with over-optimised anchor texts. That is, too many links contain anchor texts with the exact keyword you want to appear on.
Black hat is a technique that defies Google’s guidelines in various ways. Paying for links is by far the most common way. Why do websites do it? Because it works. And because white hat link building is often complicated, resource intensive and doesn’t always bear fruit.
White Hat Link Building stays entirely on the safe side of Google. This is when websites link to you, for example:
- Thanks to the quality of your content
- Through real collaborations
- Being featured on other websites and news sites in a natural way.
Many businesses use a mixture of the two strategies to maximise their impact.
10 linking strategies that work
We’ve collected some of the best linking strategies for you below. Pick your favourites and start your own link building as soon as you can.
Buying links
Buying links means that you pay a site or provider for the links you want. It’s the safest way to get backlinks, but is also an interesting watershed for SEO specialists. You can roughly divide the industry into three camps:
- Those who buy links and aren’t afraid to tell.
- Those who buy links, but don’t want to show it.
- Those who don’t buy links at all.
There is a constant discussion in and between the camps about the importance of purchased links for SEO and whether it is OK to buy, or not. The reason being that they violate Googles guidelines.
In the worst case scenario, a poorly executed link buying strategy can result in your website being penalised by Google, with lower positions in the search results. Therefore, it is important to use a link provided with knowledge and expertise in this area.
Why do people buy links?
- Because it works – if the purchased links are of sufficiently high relevance and quality. Google has not yet found a way to identify purchased links that works on a larger scale.
- Because it’s simple. Not everyone has the time or resources to familiarise themselves with white hat link building techniques. Or they’ve tried, without success. Then purchased links may feel like the only reasonable route.
- Because you can customise the target pages. It is extremely difficult to get natural links to your category/service/product pages, which are often the most important for conversion. If you buy links, you can direct them to exactly the pages on your site that you want to boost.
We’ve been working with purchased links for 13 years and have our own platform where our customers can buy their own links: Search Royals. If you’re interested, you can create a free account and see our entire range. Otherwise, we have the following packages where we take care of your link building, as well as your other SEO needs: Our SEO 360 packages
Providers
The easiest way to naturally build links is through your suppliers. Common ways they can link to you are:
- Customer pages. If they have pages where they mention their customers, you should of course be listed there.
- Reviews. Offer to write a positive review about them and add that they are welcome to present the review on their site, with a link to you as a reference. A perfect win-win situation.
- Case Study. You can appear as a reference job or a case study with the supplier, if they produce them. This is a natural opportunity to get a link.
NOTE: According to Google’s guidelines, it is forbidden to explicitly ask for links. Some people get round this by taking the discussions verbally.
The ultimate guide
Are you an expert in your field and able to create user-friendly guides? Great! It’s a way to help your users, get positive branding and build links at the same time. Here’s how:
- Problem definition: Think about what problems your users have that you can help them solve.
- Keyword analysis: Do a keyword analysis and see how common the searches are for the different problems.
- Competitor analysis: Do a competitor analysis to see what the top three ranking guides look like. Note how the guides are constructed, how many words they contain and which sites link to them.
- Bigger and better: Create a better and bigger guide than the most popular competitors and share it via social media and other channels.
- Outreach: Reach out to those who link to your competitors’ guides and tell them about your guide – it’s more current and more comprehensive.
Creating comprehensive guides can be a resource-intensive project, but the rewards are manifold if you do it right. You get a better and more helpful user experience, good branding and better SEO.
Charity
A simple and straight forward tactic to get links is to work with charities. Several organisations have lists where they mention and link to their benefactors. The closer your collaboration with the charity organisations, the greater the chance that it will talk about the collaboration in more detail. You can also create unique offers for the charity’s members or donors. Present these through your website in a user-friendly way so that it becomes an additional incentive for them to link to you.
Blog partnerships
Blog partnerships are mainly about getting bloggers in your industry to write about you and link to you. It is important to know if the blogger is linking out to the companies they are talking about and if the links are DoFollow. These collaborations will cost you something, in terms of pure money or products.
To find people who blog in your industry, you can type the following into the Google search bar:
(industry name) “blog”
See example below:

Review the different blogs to see how much value they have. Note the domain strength and whether the blog has any traffic.
NOTE: Keep in mind that, according to Google’s guidelines, it is forbidden to explicitly ask for a link.
Collaboration with other businesses and organisations
Find industries that your company has natural synergies with and create smart collaborations. This involves offering your expertise for free, or at reduced rates, to build bridges.
Example:
Let’s say you were a physiotherapist during the period when CrossFit was making waves. Then you could have contacted all the CrossFit centres in your city and offered:
- A customised and digital guide on how their members could take care of incipient joint or muscle problems. The centre could publish the guide on their website, hopefully with a reference to your website.
- A custom page on your website with special offers for the CrossFit centre’s members that they could link to.
In any industry, there are natural synergies. Find your best possible audience and think about how you can create content that is relevant to members, employees and customers on the other side.
Lectures
Map out all the places within a reasonable distance that hold lectures or seminars about your industry. Conferences work well too, of course. If you have something relevant to offer, it’s in the interest of both your brand and your SEO to attend these forums. The organisers usually have digital platforms where they talk about the events and where you as a speaker get the chance to present yourself. Take advantage of this to write an SEO-friendly text and link to your company.
Scholarships
Universities, colleges and student organisations often have very strong domains, which means their links carry a lot of weight. By announcing scholarships and doing outreach to schools and organisations, you can get them to link to you. The process is as follows:
1. Brainstorm a scholarship that is timely and relevant to your organisation.
2. Create a landing page on your site that describes:
- The scholarship – The topic and who is eligible to apply.
- How to apply.
- The closing date.
- How, where and when you will announce the winner.
- If you already have a scholarship – talk about your previous winners.
3. Make a list of universities/colleges/student organisations that might be interested.
4. Check their websites to see if they have a page on scholarships. They will usually have an email address for the relevant contact person. Do a site search on the university using: “site:universityURL scholarship” and you’ll find it faster.
5. Create a template for the mailing with all the necessary information and a pitch about why the scholarship is important. Feel free to personalise the mailing, for example if you have a previous winner from the university.
6. Send out and follow up until you receive a response.
7. Check that universities are publishing the links correctly.
8. Once you have collected the essays and selected the winners, make sure you do a winner interview. Then pitch it to the university and any other institutions where the winner is active and involved in the work. This can generate even more links in the end.
Statistics, infographics and surveys
Do you and your company have unique data and knowledge? Are you able to conduct relevant research studies in your industry? These are golden opportunities for both linking and branding.
The process looks roughly like this:
- Target audience analysis. Research your intended target audience for the research. What are they interested in? What are they talking about in relation to your niche/industry?
- Choose the topic. Find a relevant topic that you can talk about and substantiate statistically.
- Collect data. Use your own data, conduct field studies/surveys or compile external data.
- Analyse and interpret the data. For the report to have an impact, you need to come up with valuable, unique or surprising conclusions.
- Create engaging content. Use the collected data and analyses to create engaging content. This could be a beautiful infographic, a detailed report or an educational video. The main thing is that the content is appealing to your target audience. They should want to both consume and share it.
- Share the content and reach out to your target audience. Maximise the reach of your content by sharing it on social channels and pitching it directly to stakeholders via outreach.
Broken link building
Broken link building is a technical approach that involves finding broken links (404) on external pages and trying to replace them with links to your website. We are mainly interested in pages that talk about your industry.
How does it work?
Pages disappear all the time, for various reasons. Domains are shut down, content is moved or removed. You can take advantage of this and do a good deed at the same time.
Example:
A page about baking links to various recipes on other sites, but half of the recipe pages don’t work (404). You realise this, contact the site’s administrator and say:
“Hey, I really like your baking page, but I see that half of your recipe links don’t work. If you want, check out these five favourite recipes on my blog, maybe one of them can replace the broken links?”.
Pretty sympathetic, right? You’ll both win in the end.
What you need is:
- Ways to find pages to investigate for broken links. You can try typing the following commands into Google for inspiration:
- “your keyword” + links
- “your keyword” + tips
- “your keyword” + inurl:links
- “your keyword” + inurl:links
- Tools to find broken links, such as ahref’s free tool.
- An articulate and sympathetic outreach email.
See example below from the search “recipe inurl:lankar”:
With the right process and a friendly email, you’ll make great contacts, get good links and even traffic from the other websites.
Setting up a linking strategy
There you go: a set of link building strategies for you to use. Now, it’s time to take action. List and prioritise the techniques that make the most sense for you, and start researching the possibilities.
Set goals
What do you want to achieve with your linking strategy? Is it to raise the authority of your entire site or of certain critical product/service pages? In most cases, it’s a combination of the two.
Links you get to your home page will distribute link strength throughout your site, which is good for the site as a whole. Elevating specific pages requires links directly to them. This is often a problem for pure white hat strategies – it’s often difficult to naturally get external links to product and service pages.
Review your resources
Creating good content for guides and reports is resource intensive. You first need to collect and collate the data and knowledge to be presented. You need copywriters to write the texts, designers for the graphics, and marketers and communicators to get the message across. Of course, one person can have several of these skills. Take advantage of it if you have it within your organisation.
Buying links does not require internal resources, but it is important that the person responsible is aware of what they are doing.
Prioritize
Many of the link building techniques will take time to implement, while some are lower hanging fruit. For example, getting links from your partners and suppliers should be faster than projects like writing reports and guides. Start with your strongest cards and build from there.
Give it time and follow up
It often takes time to create guides, reports and resources that are good enough to get natural links. You should be able to estimate the time taken to produce them, more or less accurately.
The hard part is assessing outreach projects where you have to convince others to refer to you.
Keep in mind that the beneficiaries of your projects should prioritise and implement what you propose, for example by adding a review, or a link to a grant. From experience, it is easy for this type of action to be deprioritised or fall through the cracks. So make sure you keep a close eye on all your projects and follow up at regular intervals if you see that the links are not appearing.
Keep track of your links
Once you have started a project, it is important to keep track of the links you receive, where they come from and their status. To do this effectively, you need an SEO tool that includes a backlink monitor. There are several good options out there, including:
Whichever one you use, it’s important that you set up a report where you see the links you expect to receive. This will help you see, among other things:
- Whether the links are nofollow or dofollow.
- Anchor texts
- If links suddenly disappear
Follow up if something doesn’t seem to be in line with your agreements.
How to measure the results of link building?
The ultimate goal of link building is to get more traffic to your website through improved positions. Along the way, it’s important to keep track of the following metrics:
- The amount of incoming backlinks. A steady influx of backlinks is good. If it’s slowing down, it’s important to understand why.
- The strength of the domains that are sending links. The stronger the domain sending links to you, the better.
- Which pages are getting links. It is important to see which pages are getting links, to understand which initiatives are working well and which are not.
- Keep the links alive. Keep track so that the links you’ve built don’t suddenly disappear for some reason.
Measure organic positions
The prerequisite for measuring the value of your work is a keyword analysis, so you know which keywords are important for different pages on your website.
The first concrete sign that the work is working is that your organic positions are improving in relation to the critical keywords. Organic positions are the unpaid search results that appear on Google and other search engines, often below the adverts. The higher the positions, the better.
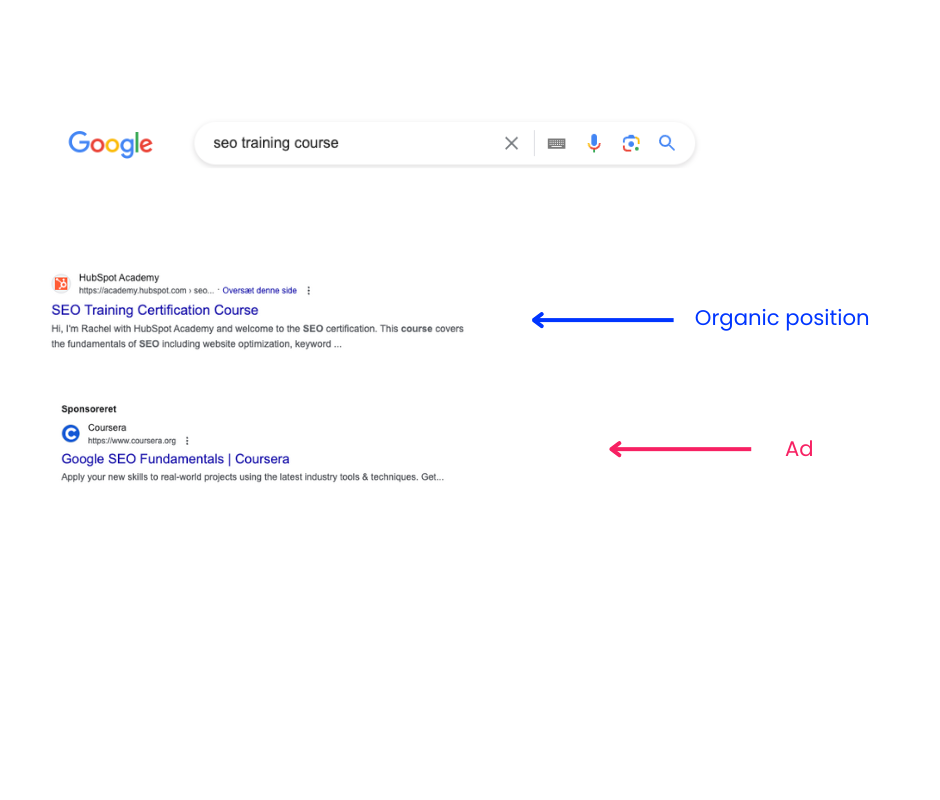
We start by looking at positions and not traffic, as your keywords may start on page 8 of Google. They won’t generate traffic until they reach the first page, but we need to know that they are steadily moving towards the top.
You can look at the positions manually in the search results and record how they move over time, but this is extremely time-consuming and inefficient.
The best way is to use a keyword tool, such as eye10, ahrefs or SEMRUSH, in which you can set which keywords are important to you. This will provide you with ongoing reports on your entered keywords. Alternatively, you can use Google Search Console (GSC), but that requires more manual labour.
You should also look at how positions on your website move in general, i.e. all your keywords. To get relevant data for this, a keyword tool is required.
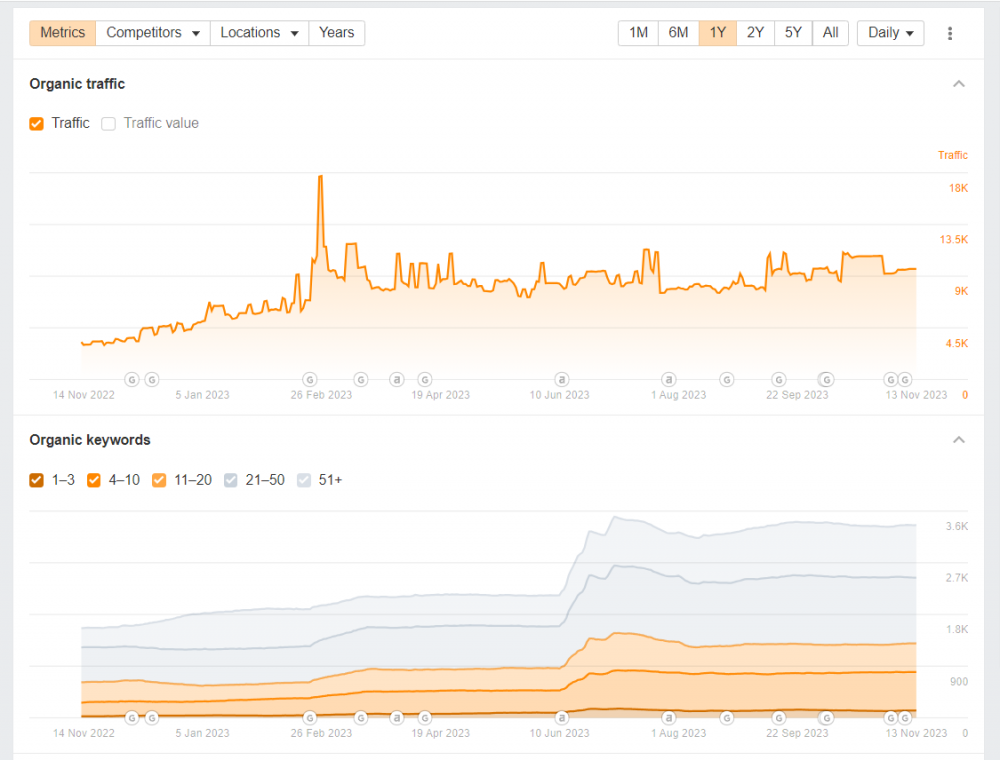
Graphs from Ahrefs showing the development of organic traffic and positions for an entire site.
Attribution
It can often be difficult to attribute the movement of positions to a single cause. SEO is affected by several aspects on and off the site:
- Links
- Updating content
- Change of navigation and internal linking
- Competitors’ activities
- Algorithm updates
What you’re looking for is a correlation between your increasing links and an increase in positions. That’s as close to proof as you can get that your link building is bearing fruit. Just keep in mind that the effect of the links may be delayed. That is, it may take a while, months even, before you start to see your positions move upwards.
If you’ve built links to a specific page and/or keyword, it’s important to keep track of them separately from the overall movement of the site. Your site’s positions may be generally steady, but your critical keyword is going up. That is also a success.
Increased traffic
By far the most important metric is the increase in organic traffic to your website, i.e. the traffic you get for free from search engines. To measure this in a relevant way, you need to use different tools together:
- Google Analytics – GA
- Google Search Console – GSC
- Other keyword tools
Google Analytics – GA
With GA, you can see the development of the number of organic visitors to your site as a whole, as well as break down the data and look at specific pages.
If you’ve built links on behalf of your entire site, you want to make sure that traffic goes up in general. If you have only targeted specific pages, you should break the report down into parts and show their traffic separately.
GA shows all visits and what visitors did on your site, but it doesn’t provide any information on what keyword they used to find you. That requires Google Search Console.
Google Search Console – GSC
GSC provides you with information about what visitors have written before visiting different pages on your website, but it does not give you a complete picture. The tool anonymises up to 50% of the visits. In this way, GA and GSC complement each other:
- GA provides the total number of visitors.
- GSC gives an indication of the most common keywords that generate traffic.
Keyword tools
Keyword tools are relevant even after you start getting traffic. They provide an ongoing report on:
- Movements in positions – You want to keep climbing towards position 1. If you start dipping, you should react.
- Estimated traffic – If you are getting less traffic than expected for a particular keyword, your search results may need to be optimised. Look at the Meta Title, Meta Description and the possibility of Rich Results. Read our guide to keyword optimisation here.
- Competitor analysis – If your competitors are acquiring links to their corresponding pages.
Set up a combined report in, for example, Looker Studio or another measurement tool so that you can easily keep track of all parameters in the same place.
Should I do link building?
If you want more traffic to your site, the answer is simple; yes! Links are one of the most important ranking factors for Google. Without them, you will never be seen.
Which strategy and techniques will work best for you depends on your circumstances.
Feel free to use the techniques listed above, or contact us for a free consultation.


